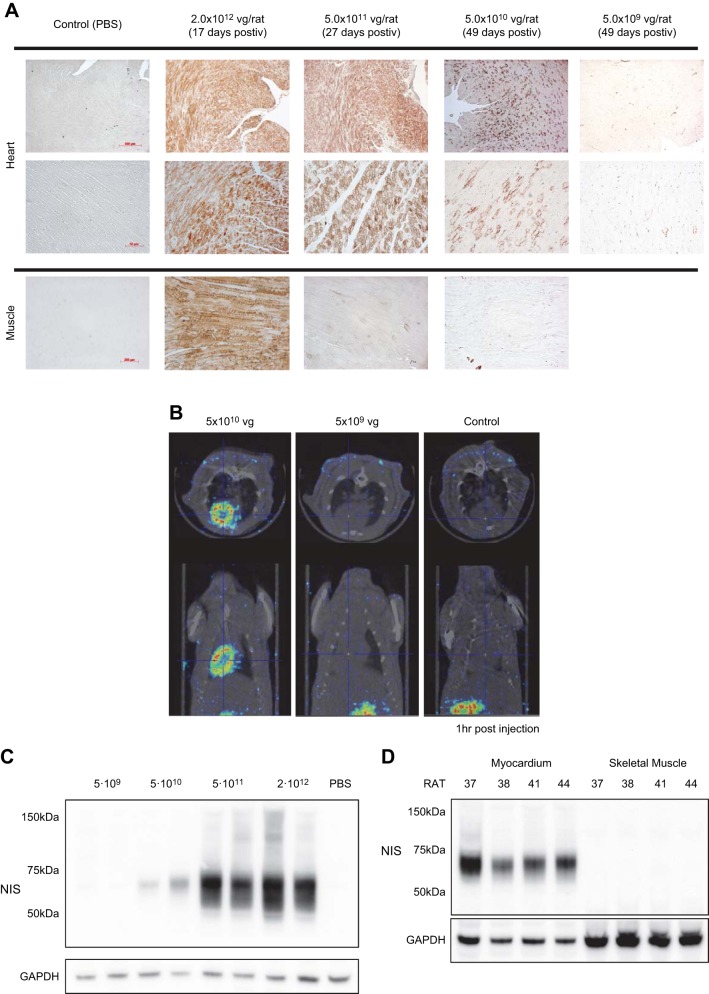
Fig. 1.
Adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9)-rat sodium-iodide symporter (rNIS) dose-finding study to produce cardiac-selective NIS expression. A: representative left ventricular [LV; ×5 (top) and ×20 (bottom) magnification] and skeletal muscle (×10 magnification) samples stained for rNIS (brown) for different doses of AAV9-rNIS. Doses of AAV9-rNIS ≥5 × 1011 vg showed saturated rNIS expression in the myocardial cells with marked (2 ×1012 vg) or mild (5 × 1011 vg) skeletal muscle expression. A dose of 5 × 1010 vg achieved heart-specific rNIS expression, while 5 × 109 vg revealed no detectable cardiac rNIS staining. B: SPECT/CT imaging 1 h after 125I administration showed robust 125I uptake in the heart with 5 × 1010 vg, whereas no cardiac signal was seen with 5 × 109 vg. C: cardiac NIS protein was not detectable by Western blot analysis with 5 × 109 vg of AAV9-rNIS, but dose-dependent increases were detected with 5 × 1010 to 2 × 1012 vg. Data are from 2 rats for each dose. D: Western blots showing robust myocardial, but no skeletal muscle, rNIS expression at the end of the study in rats from the experimental groups treated with 5 × 1010 vg of AAV9-rNIS. Data are from 4 rats.