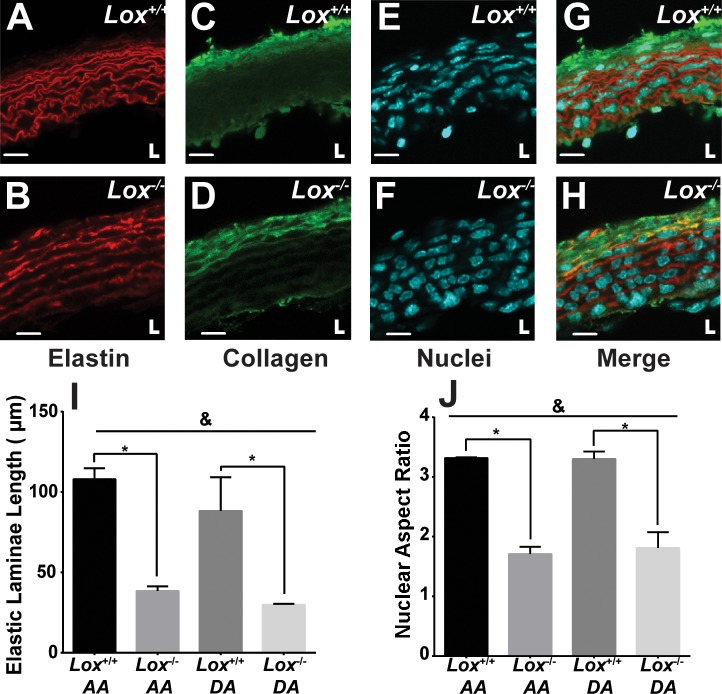
Fig. 2.
Aortic wall structure in newborn Lox mice. The elastic laminae structure in Lox+/+ (A) and Lox−/− (B) AAs showed fragmented laminae in Lox−/− compared with Lox+/+ mice. Collagen staining in Lox+/+ (C) and Lox−/− (D) AAs showed abundant adventitial collagen in both genotypes. Nuclear staining in Lox+/+ (E) and Lox−/− (F) AAs showed more rounded nuclei in the Lox−/− AA compared with the Lox+/+ AA. G and H: composite images of Lox+/+ (G) and Lox−/− (H) AAs. L indicates the location of the vascular lumen. Scale bars = 10 µm. I: quantification of the uninterrupted elastic laminae length confirmed elastic fiber fragmentation in the Lox−/− AA and DA. J: quantification of the nuclear aspect ratio confirmed altered cellular organization in the Lox−/− AA and DA. n = 3 images/group, with at least 8 elastic laminae and 20 nuclei per image analyzed. &Genotype accounted for significant variance between groups (P < 0.05). *Groups were significantly different from each other (P < 0.05).