Figure 5.
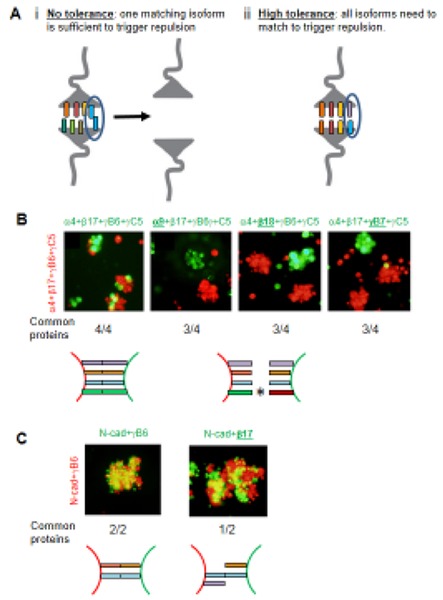
Tolerance and Interference. A) Schematic diagrams illustrating two extreme ‘tolerance to common isoforms’ levels. i) With no tolerance the recognition of one isoform in common between two interacting neurons is sufficient to mediate Pcdh recognition and to trigger repulsion even when all other isoforms are different. ii) With high tolerance one Pcdh mismatch between two interacting neurons is sufficient to interfere with Pcdhs recognition and ultimately repulsion even if all other Pcdhs isoforms are the same. B) Aggregation assays with K562 cells transfected with four Pcdh isoforms labeled in green or red. The underlined isoform in green indicates a mismatched isoform between the red and the green cells, which, as can be seen, results in the red and green cells forming separate aggregates. Experiments with two to five transfected isoforms gave similar results [36]. C) Control assays showing that N-cadherin does not “interfere” with Pcdh adhesion.
