Figure 1. MACF1 structure and role in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
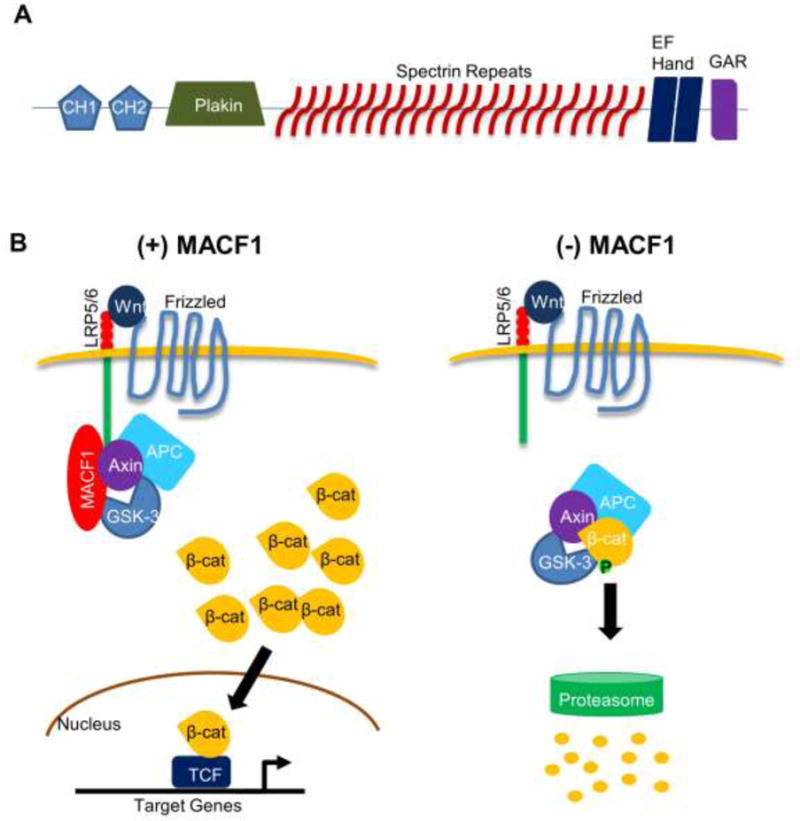
(A) General protein structure of MACF1. The five functional domains found in most MACF1 isotypes are shown: the actin-binding domain (ABD) comprised of CH1 and CH2 fragments, a plakin domain, 23 α-helical spectrin repeats, two EF hand motifs, and a GAR domain at the C-terminus. CH1: calponin homology domain 1. CH2: calponin homology domain 2. GAR: Gas2-related domain. (B) MACF1 knockdown inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Upon Wnt binding to the receptor, MACF1 translocates axin and associated molecules to the cell membrane, allowing accumulation of β-catenin in the cytosol. Some β-catenin proteins enter the nucleus to turn on target gene expression. In the absence of MACF1, Axin is unable to translocate to the cell membrane and facilitate formation of the destruction complex containing β-catenin, resulting in proteasome-mediated β-catenin degradation. LRP5/6: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6. GSK-3: glycogen synthase kinase-3. APC: adenomatous polyposis coli.
