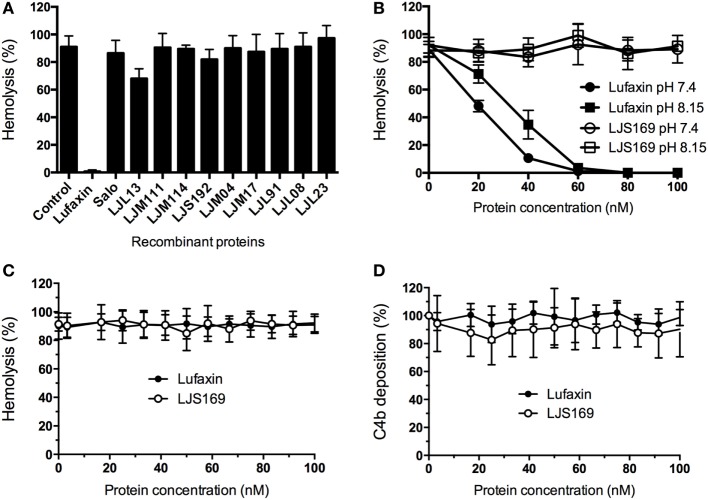
Figure 1.
Lufaxin is the alternative pathway (AP) salivary inhibitor of Lutzomyia longipalpis. (A) Recombinant salivary proteins expressed in HEK 293-F cells were tested on the AP-mediated hemolysis assay using rabbit red blood cells and normal human serum (NHS). Only Lufaxin caused significant inhibition of lysis (p < 0.001, ANOVA + Tukey test). (B) Lufaxin caused inhibition of hemolysis in a dose-dependent manner at pH 7.4 or pH 8.15. LJS169 was used as negative control as it did not present anti-complement activity. (C) Lufaxin and LJS169 were tested in the classical pathway hemolytic assay with NHS and antibody-sensitized sheep erythrocytes. Neither Lufaxin nor LJS169 inhibited hemolysis. (D) Mannan-coated microplates were used to activate the lectin pathway. Lufaxin or LJS169 was added together with NHS and incubated at 37°C. The deposition of C4 was measured using anti-C4 antibodies and no effect was seen either for Lufaxin or LJS169.