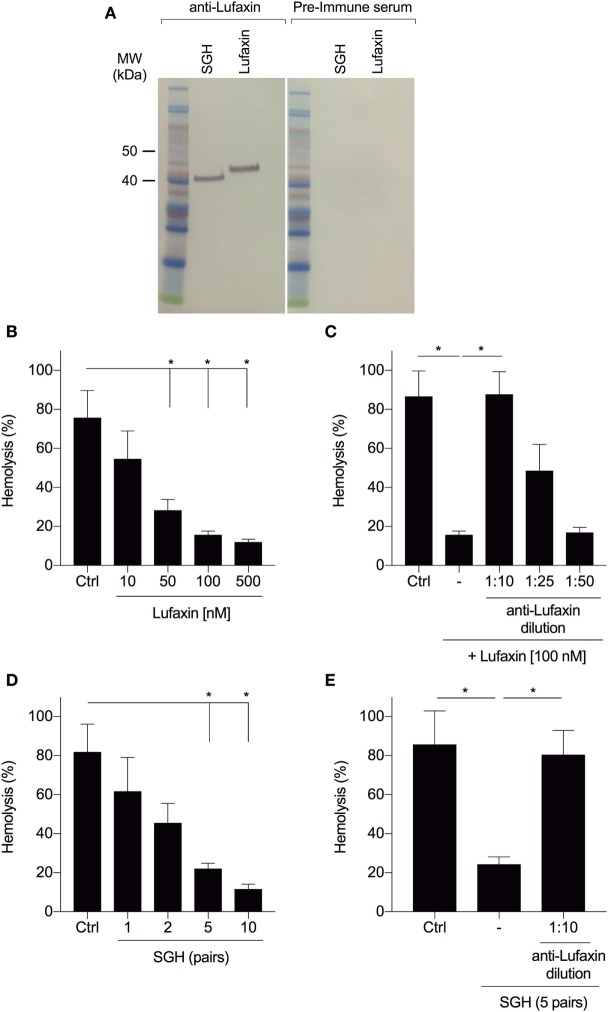
Figure 2.
Antibodies to Lufaxin block the inhibitory effect of Lufaxin and sand fly saliva on the AP of complement. (A) Anti-Lufaxin serum recognizes both recombinant Lufaxin (500 ng) and native Lufaxin on Lutzomyia longipalpis salivary gland homogenate (SGH – five pairs). Lufaxin or SGH was loaded in a NuPAGE 4–12% gel, followed by Western blotting using anti-Lufaxin polyclonal antibody. Mice preimmune serum was used as negative control. (B) AP hemolytic assays were carried on with different concentrations of Lufaxin. (C) Lufaxin (100 nM) was preincubated with different dilutions of anti-Lufaxin serum for 10 min and tested on AP-hemolytic assays. (D) AP-hemolysis assays were carried out with different amounts of L. longipalpis pairs of SGH. (E) L. longipalpis SGH (5 pairs) were preincubated with anti-Lufaxin serum (1:10) for 10 min and tested on AP-hemolytic assays. (B–E) 5 × 106 rabbit erythrocytes were incubated with normal human serum (1:20) and samples at 37°C for 30 min, and the percentage of hemolysis was quantified. PBS was used in negative controls (Ctrl). Erythrocytes incubated with distilled water were considered as 100% of hemolysis. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments.