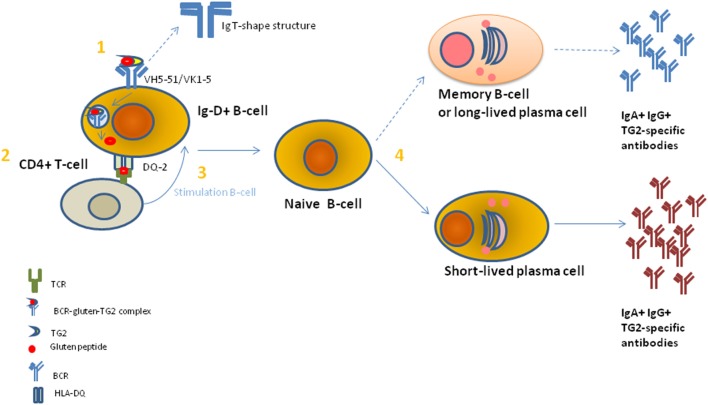
Figure 4.
A model to explain the gluten-dependent production of tissue transglutaminase 2 (TG2)-specific antibodies. (1) TG2-gliadin complexes are taken up by a TG2-specific B cell through B-cell receptor (BCR)-mediated endocytosis. BCR shows a restricted use of VH and VK chains of IgD+ istotype. Then, BCR-TG2 cross linked to gliadin peptides complexes are endocytosed and transported to the cellular endosomal compartment where gliadin peptide deaminated by TG2 enzyme were release to bind human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ specific molecules for CD4+ T-cell presentation. (2) CD4+ T-cell-recognize gliadin peptide presented by HLA-DQ molecule through a specific T-cell receptor (TCR). Correct TCR-peptide interaction causes the signal for B-cell stimulation. (3) B-cell stimulation of IgD+ naïve B-cells leads to the induction of immunoglobulin (Ig) mutation and class switching. (4) Naïve B-cells differentiate in short-lived plasma cells (PCs) (preferentially) and long-lived PCs or memory B cells and release IgA+ and IgG+ TG2-specific antibodies.