Figure 5.
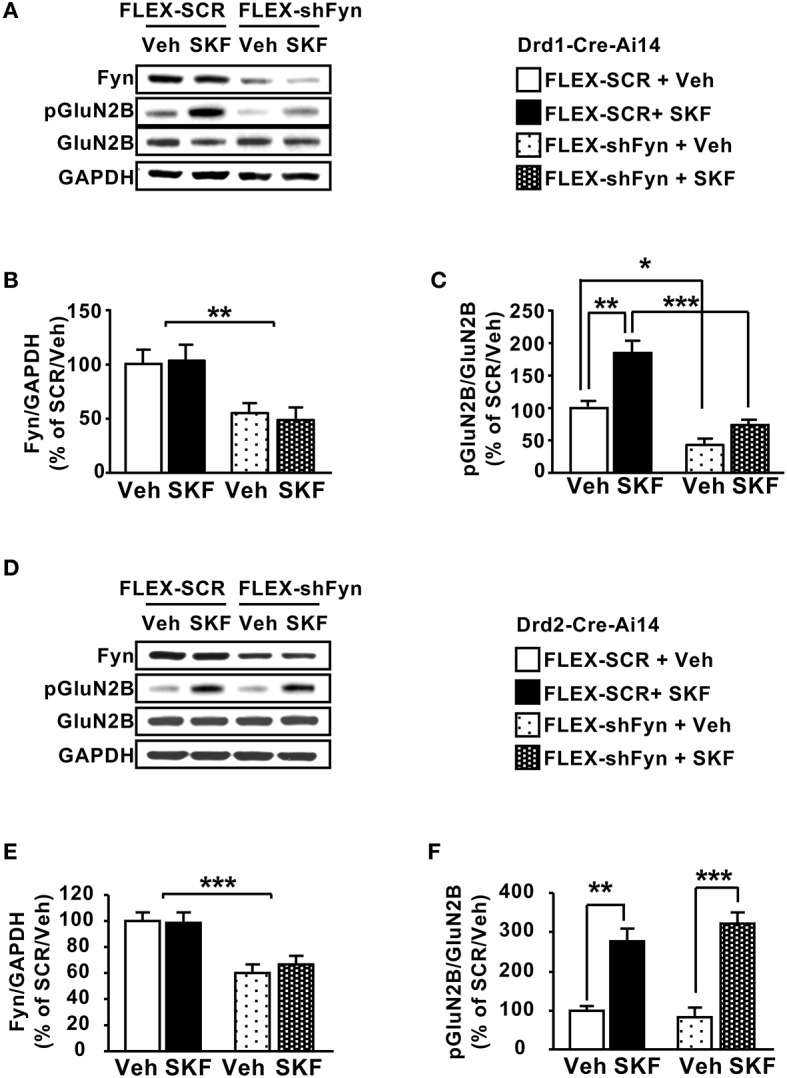
Knockdown of Fyn in DMS D1R but not in D2R neurons attenuates SKF81297-dependent GluN2B phosphorylation. (A–C) The DMS of Drd1-Cre-Ai14 mice (A–C) or Drd2-Cre-Ai14 (D–F) was infected with Ltv-FLEX-shFyn or Ltv-FLEX-SCR (2 × 107 pg/ml). Four weeks later and 15 min before the dissection, animals received a systemic administration of SKF81297 (SKF, 5 mg/kg) or vehicle (Veh, 2% DMSO). The levels of Fyn (A,B,D,E), phosphoTyr1472[GluN2B] (pGluN2B) and GluN2B (A,C,D,F) as well as GAPDH were analyzed by western blot analysis. (A,D) Representative images of the western blot analysis. (B,C) Quantification of Fyn knockdown (B) and GluN2B phosphorylation (C) in Drd1-Cre-Ai14 mice. Data are presented as the mean densitometry value of Fyn divided by the mean densitometry values of GAPDH ± SEM (B) or as the mean densitometry value of pGluN2B divided by the mean densitometry values of the total GluN2B ± SEM (C) and expressed as % of the mean value of FLEX-SCR/Vehicle. (B) Two-way ANOVA showed a main effect of shFyn [F(1, 12) = 9.507, p = 0.0095], no effect of SKF treatment [F(1, 12) = 0.03439, p = 0.85], and no interaction [F(1, 12) = 0.1446, p = 0.71]. (C) Two-way ANOVA showed a main effect of shFyn [F(1, 12) = 49.24, p < 0.001], a main effect of SKF treatment [F(1, 12) = 26.24, p = 0.0003], but no interaction [F(1, 15) = 6.36, p = 0.023], and post-hoc Tukey's multiple comparison test showed a significant effect of SKF within the FLEX-SCR groups (SCR/Veh vs. SCR/SKF, p < 0.01), and a significant effect of shFyn within the vehicle groups (SCR/Veh vs. shFyn/Veh, p < 0.05) and within the SKF-treated groups (SCR/SKF vs. shFyn/SKF, p < 0.001). (E,F) Quantification of Fyn knockdown (E) and GluN2B phosphorylation (F) in Drd2-Cre-Ai14 mice. Data are presented as the mean densitometry value of Fyn divided by the mean densitometry values of GAPDH ± SEM (E), or as the mean densitometry value of pGluN2B divided by the mean densitometry values of the total GluN2B ± SEM (F) and expressed as % of the mean value of Lenti-FLEX-SCR/Vehicle. (E) Two-way ANOVA showed a main effect of shFyn [F(1, 16) = 26.06, p = 0.0001], no effect of SKF treatment [F(1, 16) = 0.1649, p = 0.69], and no interaction [F(1, 16) = 0.3032, p = 0.58]. (F) Two-way ANOVA showed a main effect of SKF treatment [F(1, 16) = 63.21, p < 0.001] but no main effect of shFyn [F(1, 16) = 0.297, p = 0.593], and no interaction [F(1, 16) = 1.506, p = 0.238], and post-hoc Tukey's multiple comparison test showed a significant effect of SKF within the FLEX-SCR groups (SCR/Veh vs. SCR/SKF, p < 0.01) and within the FLEX-shFyn groups (shFyn/Veh vs. shFyn/SKF81297, p < 0.001). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. (A–C) n = 4 and (D–F) n = 5.
