FIGURE 1.
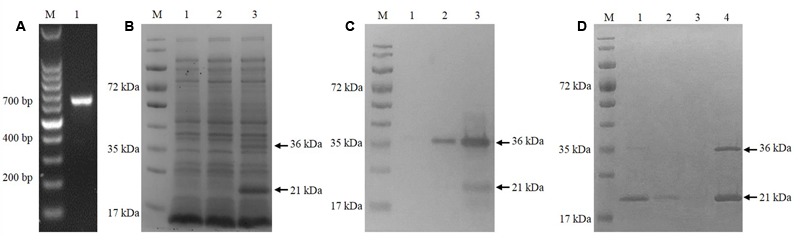
Expression of recombinant MEDLE-2 protein in Escherichia coli. (A) PCR amplification of the cgd5_4590 gene in C. parvum. Lane M: 100-bp molecular makers; Lanes 1: cgd5_4590 PCR product. (B) Expression of recombinant MEDLE-2 protein in E. coli BL21 (DE3) revealed by SDS–PAGE analysis. Lane M: protein size makers; Lane 1: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a vector control; Lane 2: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a-cgd5_4590 without IPTG induction; Lane 3: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a-cgd5_4590 with IPTG induction. (C) Expression of recombinant MEDLE-2 protein in E. coli BL21 (DE3) revealed by Western blot analysis using Anti-His tag. Lane M: protein size makers; Lane 1: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a vector control; Lane 2: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a-cgd5_4590 without IPTG induction; Lane 3: lysate from bacterial cells transformed with pET28a-cgd5_4590 with IPTG induction. (D) Purity of recombinant MEDLE-2 revealed by SDS–PAGE analysis. Lane M: protein size makers; Lane 1: the first volume of washing solution with 20 mM imidazole from the purification column; Lane 2: the fifth volume of washing solution with 20 mM imidazole from the purification column; Lane 3: the eighth volume of washing solution with 20 mM imidazole from the purification column; Lane 4: target protein eluted from the purification column using 250 mM imidazole.
