Fig. 1.
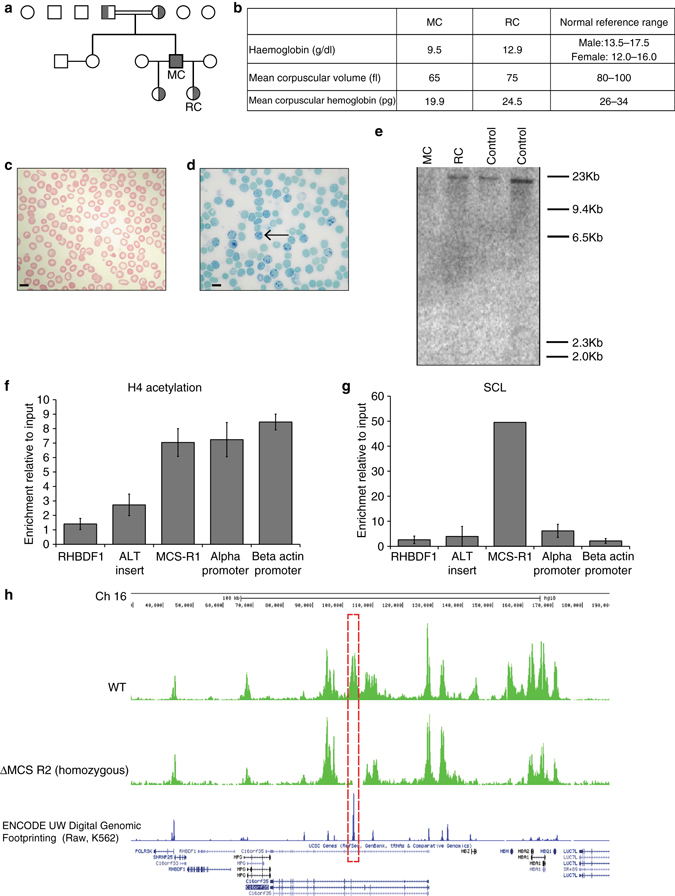
Characterization of a rare natural mutation ((αα)ALT) confined to MCS-R2. a Kindred showing patient (MC) homozygous for the (αα)ALT mutation and his heterozygote daughters. b Hemoglobin level and red cell parameters of MC and RC (who is heterozygous for the (αα)ALT mutation). c Peripheral blood smear, Giemsa stained, from patient MC, which shows anisocytosis and poikilocytosis with some irregularly contracted cells; scale bar represents 10 μm. d Peripheral blood Hemoglobin H (HbH) preparation, brilliant cresyl blue stained, from patient MC, which shows HbH inclusions; scale bar represents 10 μm. e Southern blot analysis using a probe specific for the core of MCS-R2, which gives an 19 kb band on BglII digest genomic DNA from normal controls and RC but not from MC confirming the absence of this segment. f, g Analysis of enrichment of histone 4 (H4) acetylation f and SCL g by ChIP-qPCR in in vitro differentiated primary erythroid cells (Fibach culture35) of MC harvested at intermediated erythroblasts stage (day 8–10 of Phase 2). The y-axis represents enrichment relative to ChIP input, normalized to 18S control region. Mean values are presented and error bars represent SD (n = 3). Amplicons are labeled thus: RHBDF1, intronic amplicon within the Rhomboid gene RHBDF1, used as a negative control; ALT insert, amplicon specific for 39 bp insert; MCS-R1, the human MCS-R1 which is one of the other enhancers of α-globin; alpha-promoter, α-globin promoter; beta actin promoter, a control amplicon over the β-actin promoter. h Analysis of the abundance of panH4 acetylation across the α-globin locus by ChIP-seq in in vitro differentiated primary erythroid cells harvested at intermediated erythroblasts stage from patient MC (lower track) and a normal control (upper track), showing the absence of the peak over MCS-R2 in patient MC (red dashed box)
