Fig. 3.
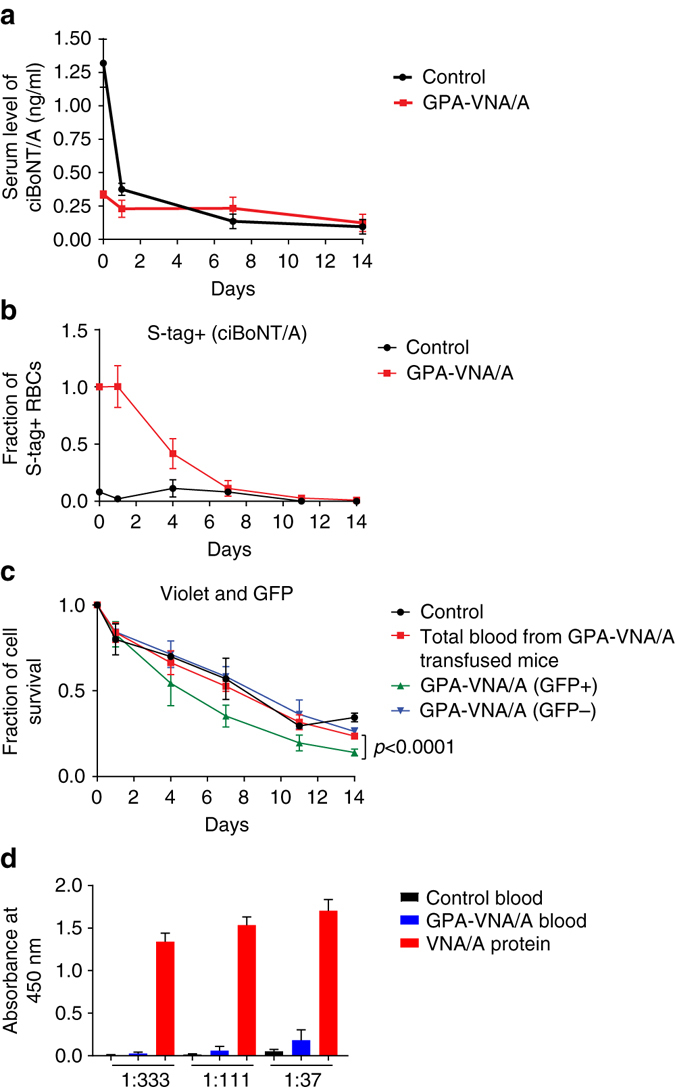
No detrimental side effects in mice injected with engineered RBCs. a Detection of serum persistence of unbound ciBoNT/A in the circulation. In all, 2 ng ciBoNT/A was incubated with 200 μl violet-stained RBCs expressing the control vector or GPA-VNA/A before they were transfused into recipient mice. The sera was collected at intervals and the amount of unbound ciBoNT/A in the serum was measured by ELISA (n = 3/group, mean ± S.E.M.). b, c Detection of RBC-bound ciBoNT/A and transfused RBCs in the blood of recipient mice. In all, 200 μl blood from wild-type mice and from mice transplanted with GPA-VNA/A expressing RBCs was stained with violet-trace dye and incubated with 1 μg ciBoNT/A before transfusion into mice. Recipients were bled at the indicated time points. RBCs were subjected to flow cytometric analyses to quantify the violet trace (total transfused RBCs, panel c), GFP (virus-transduced cells, b), and S-tag (indirectly detecting RBC-bound ciBoNT/A, panel b) (n = 3/group, mean ± S.E.M.). In Fig. 2c, the GPA-VNA/A RBCs measures total RBCs from GPA-VNA/A chimera mice, which are a combination of non-transduced (~97%) and transduced cells (~3%). To further distinguish the transduced cells, we gated on the GFP+ (GPA-VNA/A) RBCs and GFP− populations (control RBCs). The difference between the GFP+ and GFP− curves is statistically significant by ANOVA two-tailed analysis. d As detailed in the Methods section, mice received three injections of control blood, GPA-VNA/A blood, or VNA/A protein, and relative abundance of antibody against-VNA/A in serum from these mice was examined by ELISA. Sera were diluted at the indicated ratios (n = 5/group, mean + S.E.M.)
