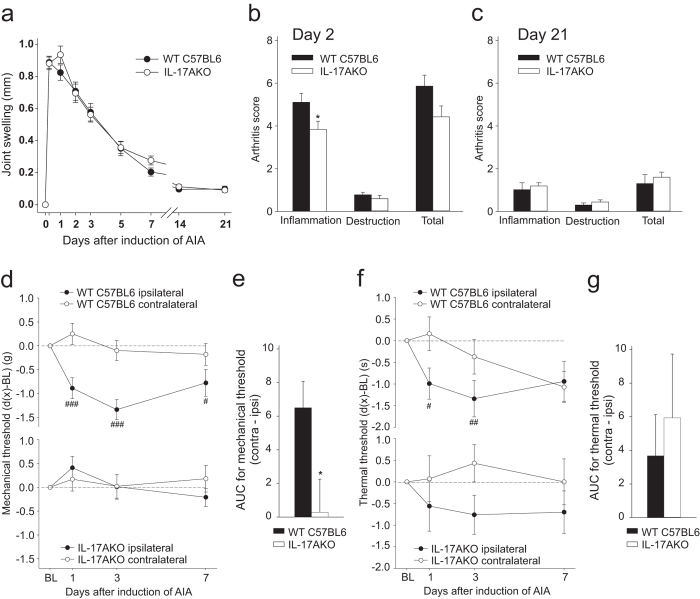
Figure 1.
Joint swelling, histopathological scoring and pain-related behaviour in wild type (WT) mice and IL-17AKO mice in AIA. (a) No significant differences in joint swelling at the injected knee were detectable in comparison of multiple experiments of WT mice and IL-17AKO mice in the course of AIA (n = 31–63 per group). (b,c) Histological examination of the inflamed knee joints from WT and IL-17AKO mice at day 2 (n = 6–23 per group) and day 21 of AIA (n = 12–16 per group) showed no significant differences in total arthritis scores between both groups of mice. (d) Hashes indicate a reduction of mechanical withdrawal threshold at the paw ipsilateral to the inflamed knee (black symbols) in WT mice (top) (n = 43). IL-17AKO mice did not show a drop of the mechanical threshold (bottom) (n = 27). (e) Areas between the ipsilateral and contralateral curves in (d) indicating the magnitude of mechanical hyperalgesia. (f) A significant reduction of thermal withdrawal threshold at the ipsilateral paw was seen in WT mice (top) (n = 34–43) whereas IL-17AKO mice (bottom) showed only a tendency of reduction of threshold (n = 27). (g) AUC from (f) indicating no significant differences in the magnitude of thermal hyperalgesia between both groups of mice. Values are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t-test), #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 (Wilcoxon’s matched-pairs signed-rank test). AIA antigen-induced arthritis, AUC area under the curve, BL baseline.