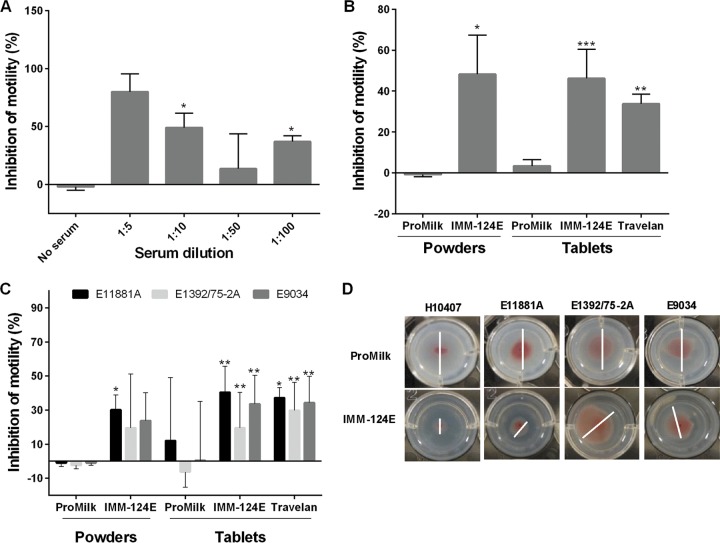
FIG 5.
BCP inhibition of ETEC motility. Bacteria were seeded at the center of wells containing CFA agar mixed with serum or BCP. Migration was determined as the distance of growth after 4 to 6 h of incubation, and percent inhibition of motility was calculated with respect to migration in no serum or ProMilk. (A) The motility assay was optimized with immune sera (at the indicated dilutions) from volunteers challenged with strain H10407. Asterisks indicate significant differences between inhibition of motility in the presence and absence of serum. (B to D) ProMilk, IMM-124E, and Travelan were tested for their capacity to inhibit ETEC motility. (B and C) Inhibition of strain H10407 motility (B) and inhibition of strain E11881A, E1392/75/2A, and E9034 motility (C). Data shown in panels A to C represent mean percent inhibition of motility plus SD from at least three experiments; values that are significantly different between HBC and ProMilk by two-sided t test are indicated by asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (D) Representative images of zones of motility of ETEC strains (white bars) in agar containing ProMilk and IMM-124E.