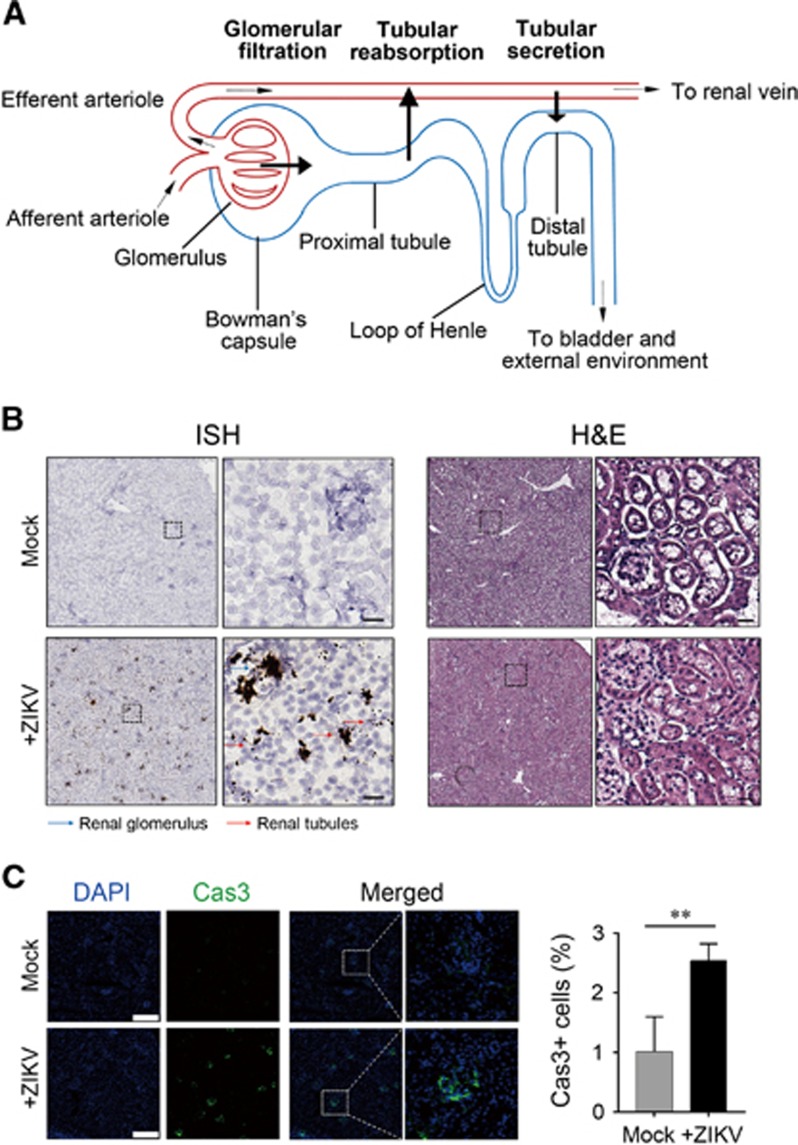
Figure 1.
Renal infection of Zika virus (ZIKV) in AG6 mice. (A) Components of the nephron. (B) Detection of ZIKV RNA in mouse kidneys. Left panel, in situ hybridization (ISH) using a ZIKV-specific probe. Blue and red arrows indicate renal glomerular and tubular cells, respectively. Hybridization signals of ZIKV RNA were developed by a chromogenic reaction and are observed as black particles. Right panel, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of caspase-3 in ZIKV-infected renal tissues of AG6 mice. Left panel, representative images. Scale bar, 200 μm. Right panel, statistical analyses of caspase-3-positive cells. **Significant difference between mock and infected cells (P<0.01; Student’s t-test).