Figure 4.
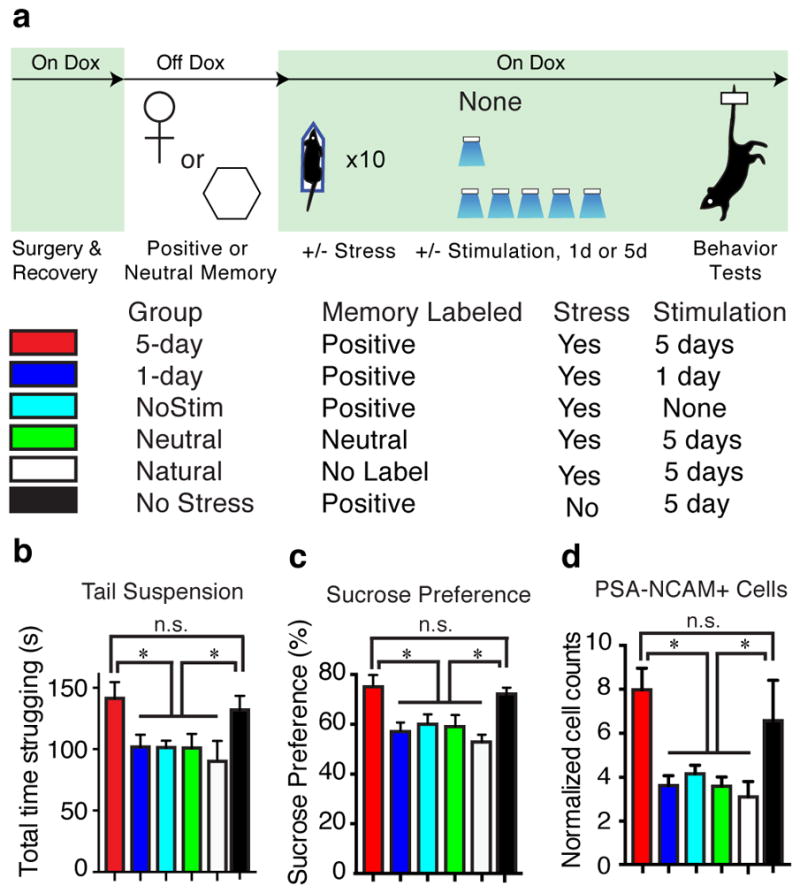
Chronic activation of a positive memory elicits a long-lasting rescue of depression-related behavior. a, Behavioral schedule and groups utilized. b, c, Animals in which a positive memory was reactivated twice a day for five days showed increased struggling in a 6-minute tail suspension test (F5, 78 = 3.34, P < 0.05) (b) and increased preference for sucrose measured over 24 hours (F5, 84 = 6.25, P < 0.01) (c). d, The 5-day positive memory stimulation group showed a significant increase of adult new-born cells in the DG as measured by PSA-NCAM+ cells (F5, 72 = 4.65, P < 0.01; See Extended Data Fig. 8 for doublecortin data and PSA-NCAM images). For these data (b–d), a one-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction of the experimental-group factor and stimulation-condition factor and was followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test. n = 14 per TST behavioral group, n = 15 per SPT behavioral group, n = 5 slices per animal for data appearing in (d). Scale bars in expanded images correspond to 5 μm. *P<0.05. Data are means +/− SEM.
