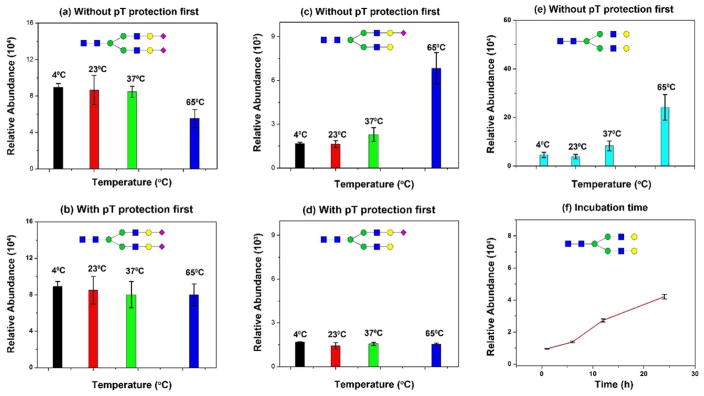
Figure 1. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of sialic acids in dimethyl sulfide (DMSO)-acetic acid (AA).
(a) Hydrolysis of native sialic acid (N2H2S2) (Sialylglycopeptide; SGP) in DMSO-AA at 4°C, 23°C, 37°C, and 65°C; (b) p-Toluidine stabilized sialic acid (N2H2S2) in DMSO-AA at 4°C, 23°C, 37°C, and 65°C; (c) Increase of N2H2S from hydrolysis of N2H2S2 in DMSO-AA; (d) No change on N2H2S due to the stabilized N2H2S2 with p-Toluidine; (e) Increase of N2H2 due to hydrolysis of N2H2S and N2H2S2 in DMSO-AA at different temperature; (f) Increase of N2H2 due to hydrolysis of N2H2S and N2H2S2 incubated 0.1% TFA from 2h to 24h (23°C). Triplicate experiments were conducted.