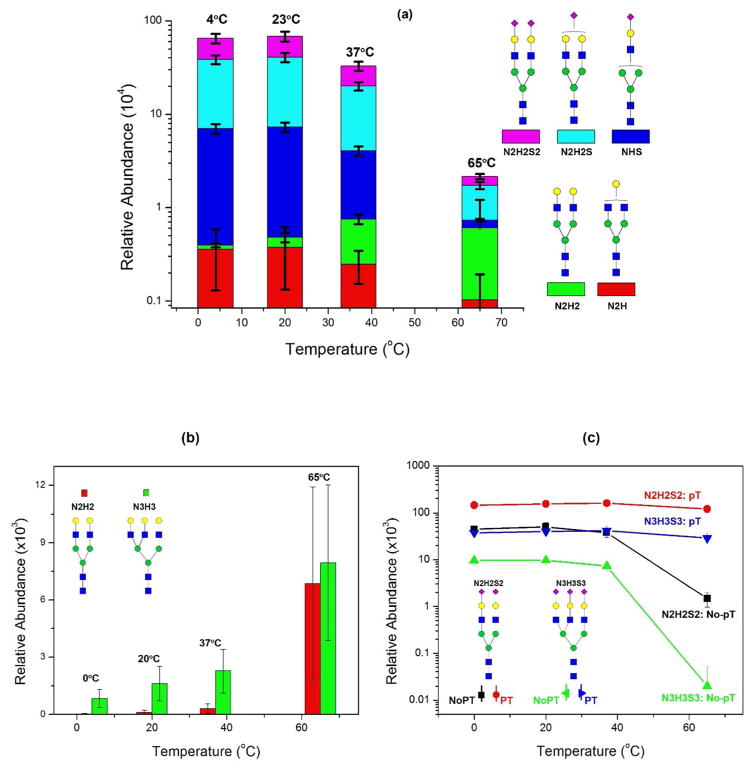
Figure 2. Effect of 0.1% TFA on the hydrolysis of Sialylglycopeptide (SGP) at different temperatures.
(a) Without hydrolysis, SGP consists of N2H2S2 only. Incubated in 0.1% TFA, it gradually hydrolyzed at low temperatures while most sialic acids were lost at an elevated temperature (65°C). SGP glycan was converted to asialo N2H2. The relative abundance was N2H2S2 (4°C) > N2H2S2 (23°C) > N2H2S2 (37°C) > N2H2S2 (65°C), while N2H2 (4°C) < N2H2 (23°C) < N2H2 (37°C) < N2H2S2 (65°C); (b) Increased asialo N-glycans in bovine Fetuin; (c) pT-stabilized sialic acids remained constant at different temperatures, while without pT, the sialic acid content was significantly reduced at an elevated temperature.