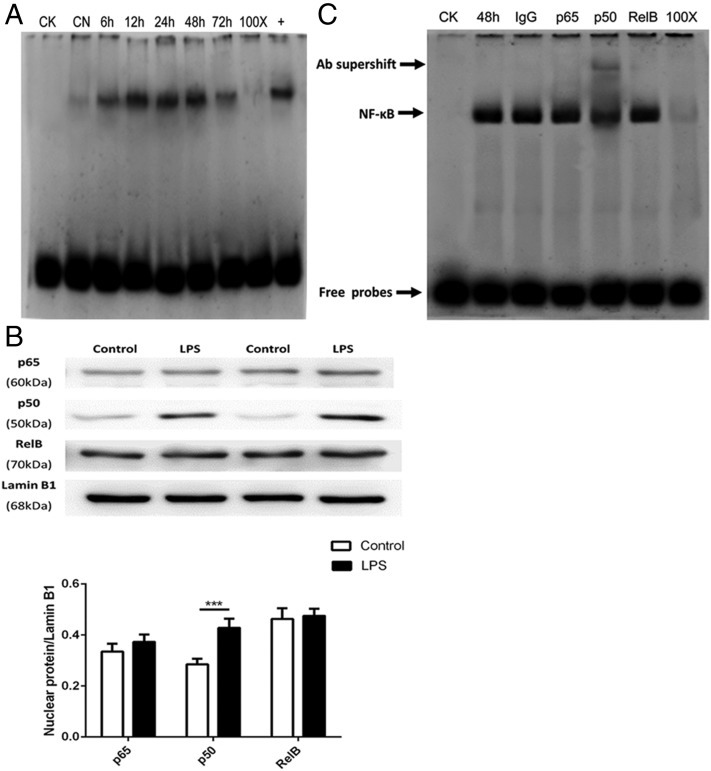
FIGURE 5.
The formation of NF-κB p50/p50 homodimers in LPS-stimulated pulmonary fibroblasts occurs during resolution phase. Primary pulmonary fibroblasts were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h or with the equivalent volume of untreated medium for the control group. After incubation, the cells were harvested to isolate nuclear protein as detailed in Materials and Methods. (A) The time course of NF-κB activation was measured via EMSA. CK, negative control; CN, control group; 100×, competition group; +, positive group. (B) The nuclear translocation of p65, p50, and RelB was assessed via Western blot and analyzed via densitometry. Values were compared with lamin B1 expression. (C) Supershift assays were performed with NF-κB p50, p65, and RelB Abs to detect the DNA binding activity of nuclear protein extracts from primary pulmonary fibroblasts obtained 48 h after LPS stimulation. The specific NF-κB bands are indicated in the polyacrylamide gel with arrows, whereas only the Ab against p50 resulted in a significant supershift. CK, negative control; 48 h, cells stimulated with LPS for 48 h; IgG, preimmune IgG as Ab negative control; p50, p50 Ab group; p65, p65 Ab group; RelB, RelB Ab group; 100×, competition group. Cells were differentiated from lung tissues harvested from six rats per condition; n = 6 per treatment per group. Data in (A) and (C) are representative of three independent experiments. Data in (B) are shown as mean ± SEM and are representative of at least four independent experiments. ***p < 0.001.