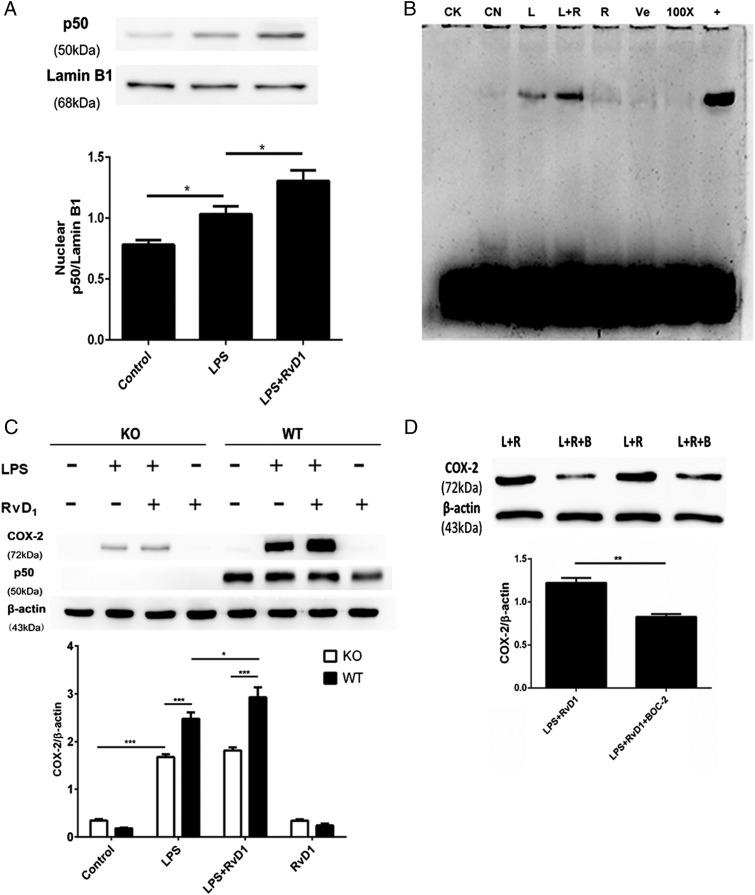
FIGURE 6.
RvD1-mediated promotion of COX-2 expression in fibroblasts is mediated by NF-κB p50/p50 activation. (A and B) Primary pulmonary fibroblasts from rats were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h, followed by the administration of 100 nM RvD1 or vehicle (0.1% ethanol) for an additional 24 h. After incubation, the cells were harvested to isolate nuclear proteins as detailed in Materials and Methods. (A) The expression of p50 in the nucleus was determined via Western blot and analyzed via densitometry. Values were compared with lamin B1 expression. (B) The activation of NF-κB was determined by EMSA assay. CK, negative control; CN, control group; L, LPS group; L+R, LPS plus RvD1 group; R, RvD1 group; Ve, vehicle group; 100×, competition group; +, positive group. (C) Primary pulmonary fibroblasts from NF-κB p50 KO (open bars) and WT mice (filled bars) were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h followed by administration of 100 nM RvD1 or vehicle (0.1% ethanol) for an additional 24 h. After incubation, the cells were harvested and sonicated to obtain the whole protein. The expression of COX-2 and p50 was determined via Western blot. (D) Primary rat pulmonary fibroblasts were incubated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 24 h, followed by the administration of 100 nM RvD1 for an additional 24 h; 10 μM BOC-2 was administered 30 min prior to the RvD1 treatment. After incubation, the cells were harvested and sonicated. COX-2 expression was assessed via Western blot. L+R, LPS plus RvD1 group; L+R+B, LPS plus RvD1 plus BOC-2 group. Cells in (A), (B), and (D) were differentiated from lung tissues harvested from six rats per condition. Pulmonary fibroblasts in (C) were differentiated from five mice per condition; n = 5–6 per treatment per group. Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are representative of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.