Figure 1.
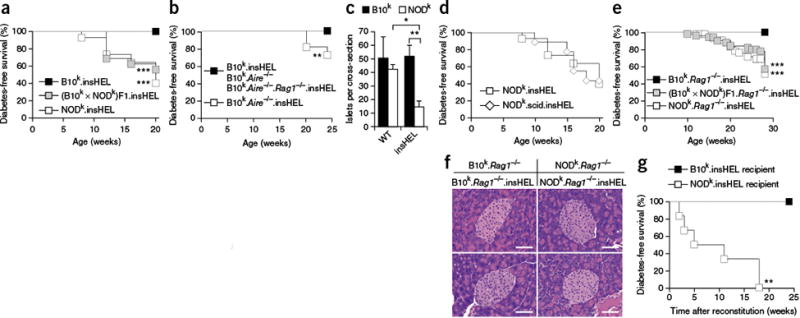
NOD mouse susceptibility to immune-independent diabetes demonstrated through a sensitized transgenic model. (a) Incidence of diabetes in male insHEL transgenic mice on the B10k (n = 22), NODk (n = 43) and (B10k × NODk)F1 (n = 16) backgrounds. No diabetes was observed in non-transgenic male littermates. (b) Incidence of diabetes in male insHEL transgenic mice on the B10k (n = 22), B10k.Aire−/− (n = 11) and B10k.Aire−/−.Rag1−/− (n = 23) backgrounds. B10k.Aire−/− mice without the insHEL transgene did not develop diabetes (n = 22). (c) Average number of islets per pancreatic section in B10k, B10k.insHEL, NODk and NODk.insHEL mice at 28 weeks of age (n = 4–5 mice/group; WT, wild type). Data are shown as means ± s.e.m. (d) Incidence of diabetes in male insHEL transgenic mice on the NODk (n = 43) and NODk.scid (n = 9) backgrounds. No diabetes was observed in nontransgenic male littermates. (e) Diabetes incidence in male insHEL transgenic mice on the B10k.Rag1−/− (n = 58), NODk. Rag1−/− (n = 44) and (B10k × NODk)F1. Rag1−/− (n = 51) backgrounds. (f) Hematoxylin and eosin histology of pancreatic islets at 28 weeks of age (representative of 7–15 mice/group). Scale bars, 50 μm. (g) B10k.insHEL mice and NODk.insHEL mice were irradiated and reconstituted with NODk or B10k bone marrow, respectively, before aging for diabetes incidence (n = 7 and 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001.
