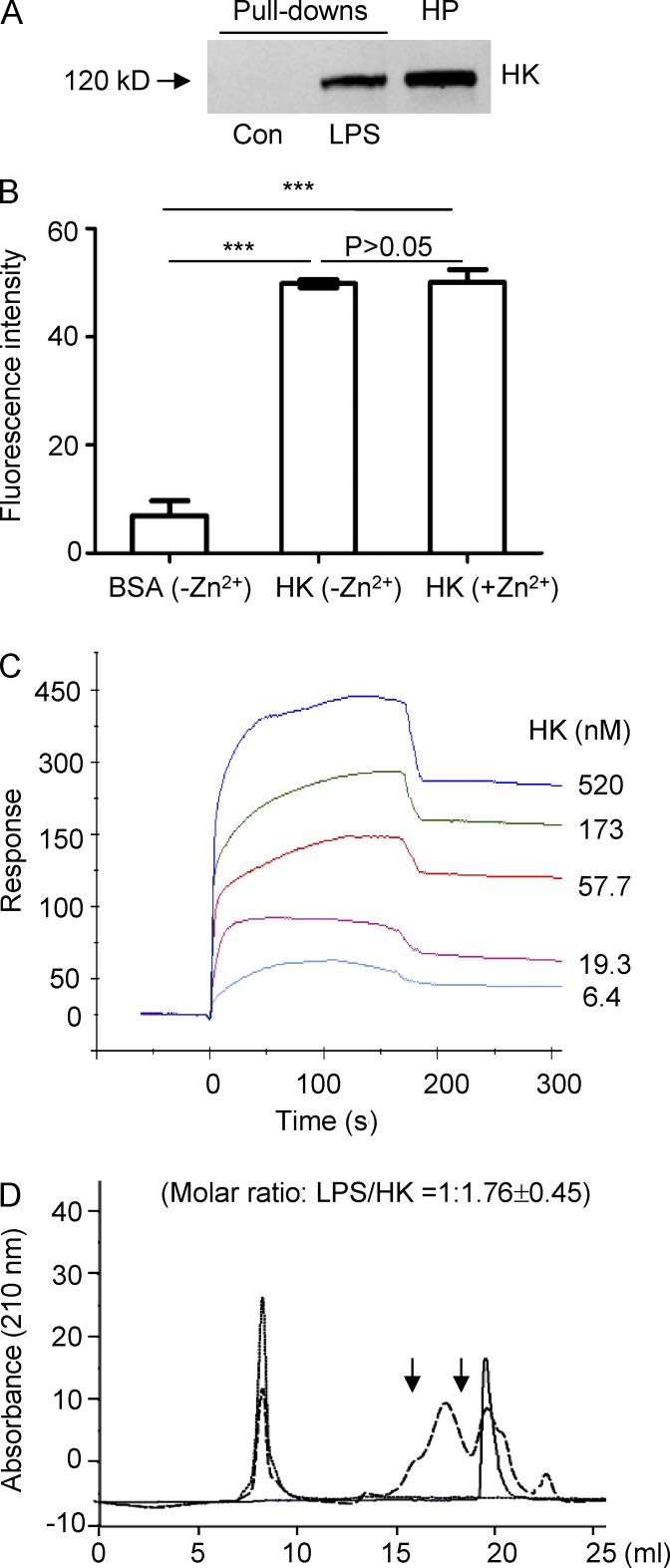
Figure 5.
HK binds to LPS with a high affinity and forms a complex in aqueous solution. (A) Forty microliters of LPS-conjugated Sepharose beads or control-Sepharose beads were incubated with 200 µl diluted human plasma (HP; 1:1 with 1× PBS) at RT for 2 h. The beads were washed three times with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100, and the associated proteins were subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-HK antibody. Data are representative of five independent experiments. (B) Ninety-six-well plates were coated with 10 µg/ml of HK or BSA and were then blocked with 2% BSA. After incubation with 100 µg/ml FITC-LPS in the presence or absence of 50 µM ZnCl2 at 37°C, the wells were washed, and fluorescence was measured. Statistical analysis was done using an ANOVA. ***, P < 0.001. Data are representative of two independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SEM. (C) Analysis of HK binding to LPS by SPR analysis revealing a binding affinity of Kd = 1.71 × 10−7 M. A representative experiment out of three independent experiments is shown. (D) FPLC profile of the HK and LPS complex. LPS (250 µg/ml) was incubated with 50 µg/ml HK at 37°C for 60 min. Samples were then loaded to the column. Samples between the two arrows were collected and subjected to measurement of protein and LPS concentrations. Solid line, HK only; dotted line, LPS only; dashed line: HK in the presence of LPS. Data are representative of three independent experiments.