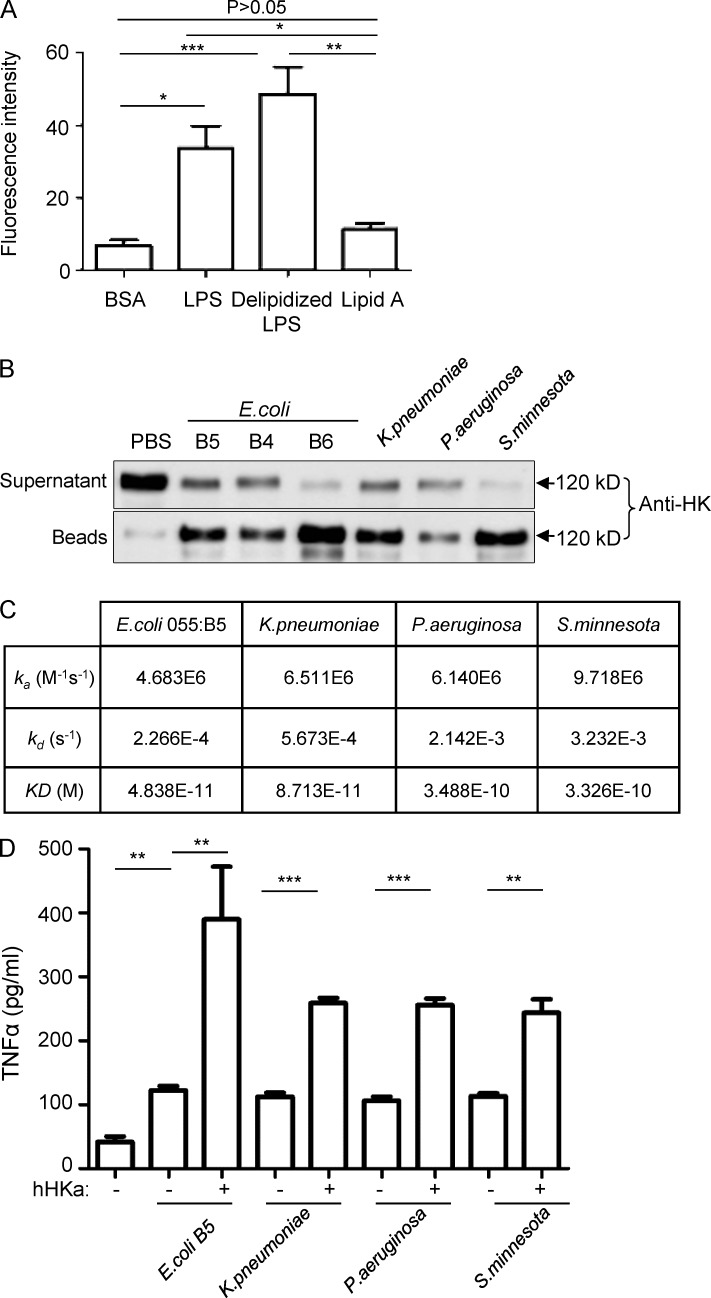
Figure 7.
HK associates with different LPS species. (A) Microtiter plate wells were coated with BSA, LPS, delipidized LPS, or lipid A at 2 µg/well. The wells were incubated with 100 nM FITC-HK for 1 h. After washing, the bound FITC-HK was quantified using SpectraMax M5. Statistics were analyzed using an ANOVA. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data are representative of two independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SEM. (B) 10 µg/ml human HK was incubated with 10 µg/ml LPS from the different sources indicated for 30 min, followed by incubation with polymyxin B beads. HK associated with beads, and in the postincubation solution, was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-HK antibody. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (C) SPR analyses of the binding of LPS from different bacteria to HKa. An HKa solution was passed over the hydrophobic HPA sensor chip that had been immobilized with one of three types of LPS isolated from K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, and S. minnesota and one type of LPS from E. coli 055:B5. An activated/deactivated flow cell was used to evaluate nonspecific binding. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Raw 264.7 cells (2.5 × 106 cells/ml) were incubated with, or without, human HKa in the presence or absence of 0.03 ng/ml different species of LPS in serum-free DMEM at 37°C for 6 h. The concentration of TNF in the culture supernatants was determined using ELISA. Statistics were analyzed using ANOVA. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data are representative of two independent experiments and expressed as mean ± SEM.