Figure 9. In vivo tumorigenicity of transformed organoids.
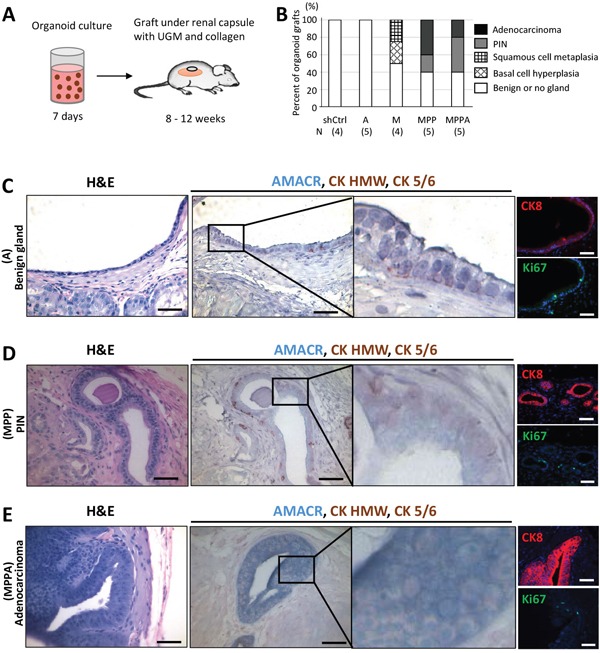
(A) Schematic representation of the process of MPPA, MPP, M, A, and shCtrl organoid transplants under the renal capsule of NOD/SCID mice. (B) Pathological analyses of organoid grafts. Grafts were stained with H&E, AMACR, CK HMW, and CK 5/6, and analyzed by a pathologist. N, number of samples analyzed. (C) Benign gland developed from A organoid transplants. Images with H&E staining; IHC staining for AMACR, CK HMW, and CK 5/6; and immunofluorescence staining for CK8 and Ki67. Blue, DAPI. (D) PIN developed from MPP organoid transplants. Images with H&E staining; IHC staining for AMACR, CK HMW, and CK 5/6; and immunofluorescence staining for CK8 and Ki67. Blue, DAPI. (E) Adenocarcinoma developed from MPPA organoid transplants. Images with H&E staining; IHC staining for AMACR, CK HMW, and CK 5/6; and immunofluorescence staining for CK8 and Ki67. Blue, DAPI. Scale bars 50 um.
