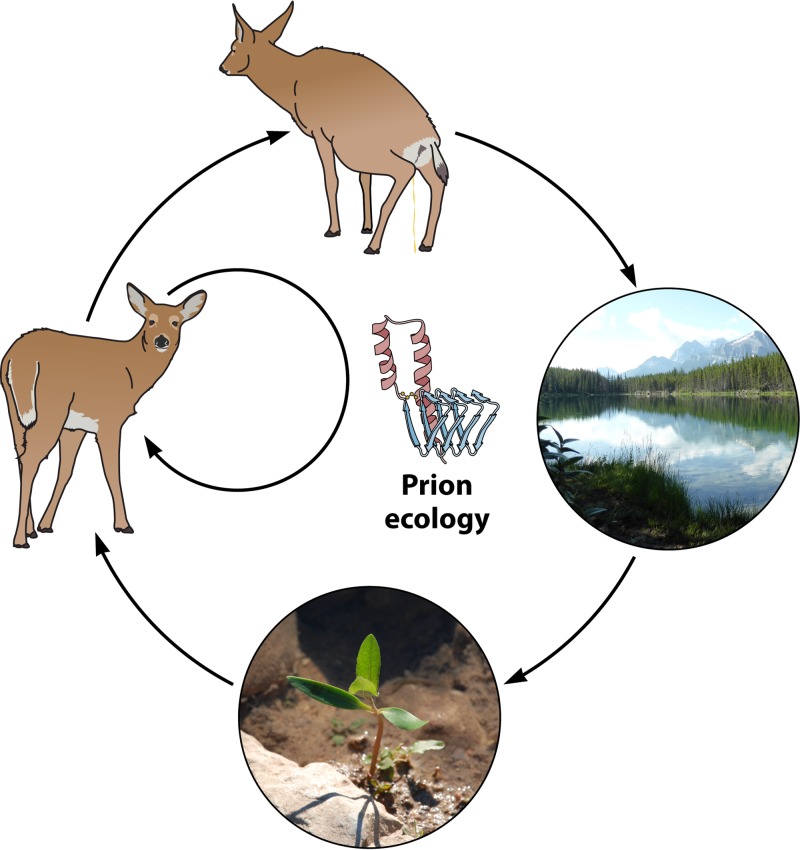
FIG 1.
CWD prion ecology. Shown is the potential movement of CWD prions in the environment. While direct transmission likely contributes the most to CWD spread, indirect transmission also occurs via CWD prion deposition into the environment from urine, feces, and saliva onto and into water, soil, and plants. Cervids and other animals likely consume prions contained in these reservoirs and become infected.