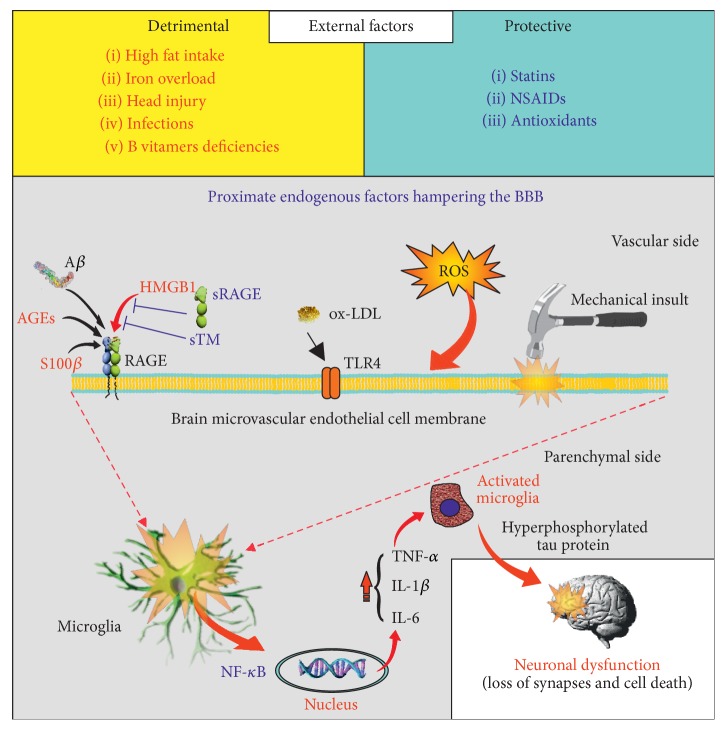
Figure 2.
Schematic based on data, both ours and others, where proximate factors generated from external sources, including dietary, infections, and injury, act on brain microvascular ECs to cause a “breach” of the BBB/NVU. The proximate factors include molecules associated with innate immune activation (DAMPs and Aβ) while agents that can interdict these factors include sTM and sRAGE. The initial and subsequent episodes of the dysfunction can “fan the flames” of neuroinflammation within the brain with microglial (and astrocytic) activation at transcriptional levels resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction, tau hyperphosphorylation, and aggregation, synapse loss, and neuronal cell death.