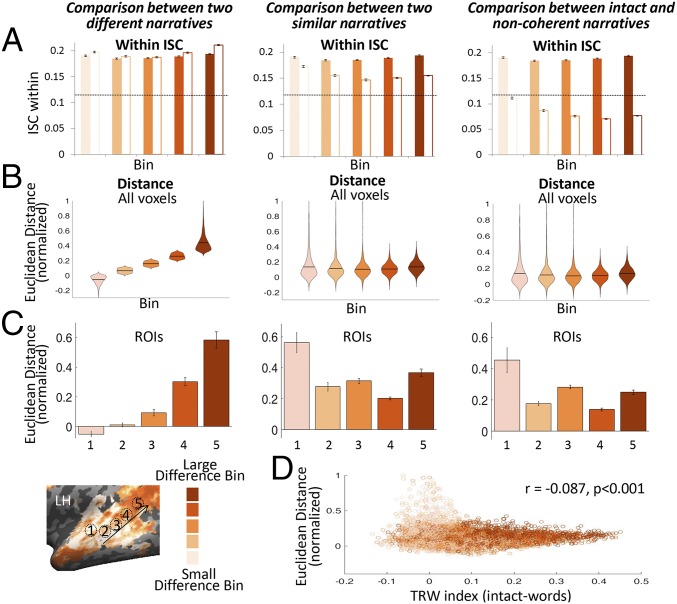
Fig. 5.
Amplification pattern is dependent on forming distinct narrative interpretations. (A) Within-subject ISC across bins for Story1 (Left, full bars) and Story2 (Left, white bars), for Story1_synonyms (Center, white bars), and for Story2_scrambled (Right, white bars). A significant ISC threshold is marked as a dotted black line. The reliability of responses within each of the intact stories was significantly above threshold, whereas reliability for Story2_scrambled was not. (B) Euclidean distance in neural response across bins between Story1 and Story2 (Left), between Story1 and Story1_synonyms (Center), and between Story1 and Story2_scrambled (Right). (C) Euclidean distance in neural response between stories in five specific regions of interest (ROIs; one from each bin) (Upper) illustrated on the brain map (Lower). (D) Scatter plot of the voxel’s TRW index and the Euclidean distance between Story1 and Story1_synonyms. The smaller the voxel’s TRW index, the larger was the difference in the neural responses between the stories.