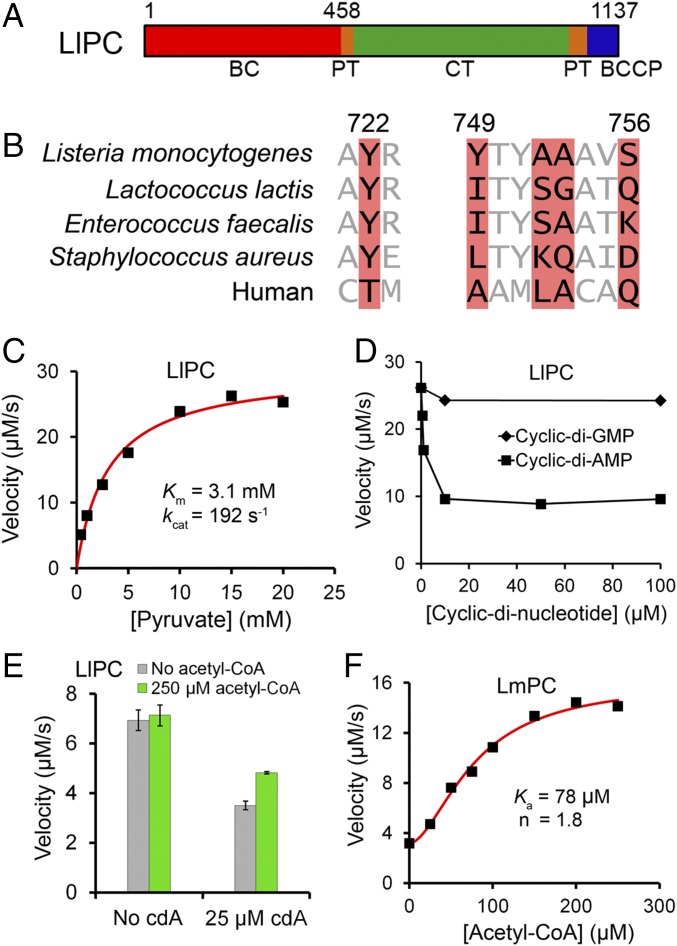
Fig. 1.
Biochemical characterization of LlPC regulation by c-di-AMP. (A) Domain organization of LlPC. The BC, CT, BCCP, and PT domains are indicated. (B) Conservation of residues in the c-di-AMP binding site of LmPC (highlighted in red). The equivalent residues in selected bacterial PCs and human PC are shown. The residue numbers are for LmPC. (C) The catalytic activity of LlPC toward the pyruvate substrate obeys Michaelis–Menten kinetics. The reaction contained 0.16 μM LlPC (measured based on monomer). (D) Inhibition of the catalytic activity of LlPC by increasing concentrations of c-di-AMP and c-di-GMP. The reaction contained 0.16 μM LlPC and 20 mM pyruvate. (E) Acetyl-CoA has essentially no effect on the catalytic activity of free LlPC, and only a small effect in the presence of c-di-AMP. The reaction contained 0.12 μM LlPC and 3 mM pyruvate. Error bars represent SDs over three separate experiments. (F) Acetyl-CoA leads to a significant activation of LmPC. The reaction contained 0.78 μM LmPC and 0.5 mM pyruvate.