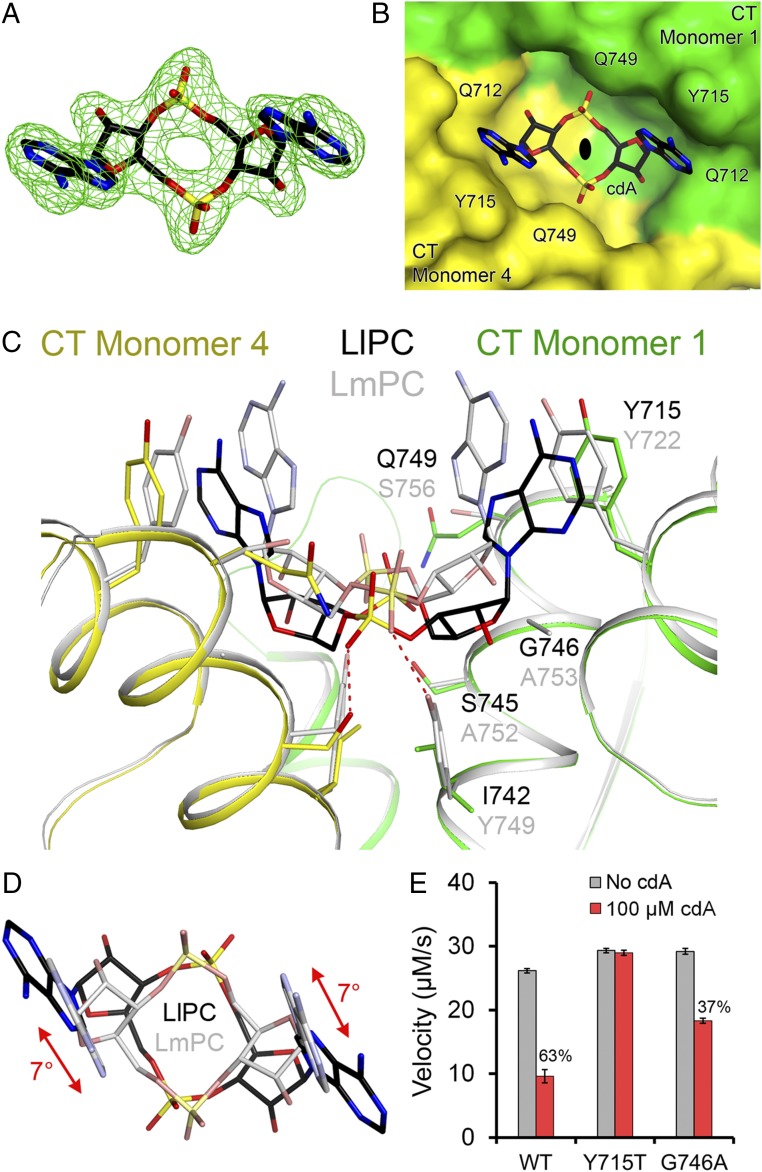
Fig. 3.
Binding mode of c-di-AMP in LlPC. (A) Omit Fo–Fc electron density at 2.3-Å resolution for c-di-AMP, contoured at 3σ. (B) Molecular surface of LlPC near the c-di-AMP binding site. The compound is bound at the CT dimer interface, and the view is down the twofold axis of this dimer, indicated with the black oval. (C) Overlay of the binding mode of c-di-AMP (black) in LlPC (green and yellow) versus that in LmPC (gray). The labels for LlPC residues (black) are placed above those for the equivalent LmPC residues (gray). (D) Overlay of the bound conformations of c-di-AMP in LlPC (black) and LmPC (gray). The view is down the twofold axis of the CT dimers. There is a rotation of the central ring of c-di-AMP in the LlPC complex relative to that in the LmPC complex. (E) Kinetic data showing that the Y715T mutant is insensitive to c-di-AMP while the G746A mutant had reduced sensitivity. The percentage inhibition for WT LlPC and the mutants are indicated. The reactions contained 0.16 μM LlPC and 20 mM pyruvate. Error bars represent SDs over three separate experiments.