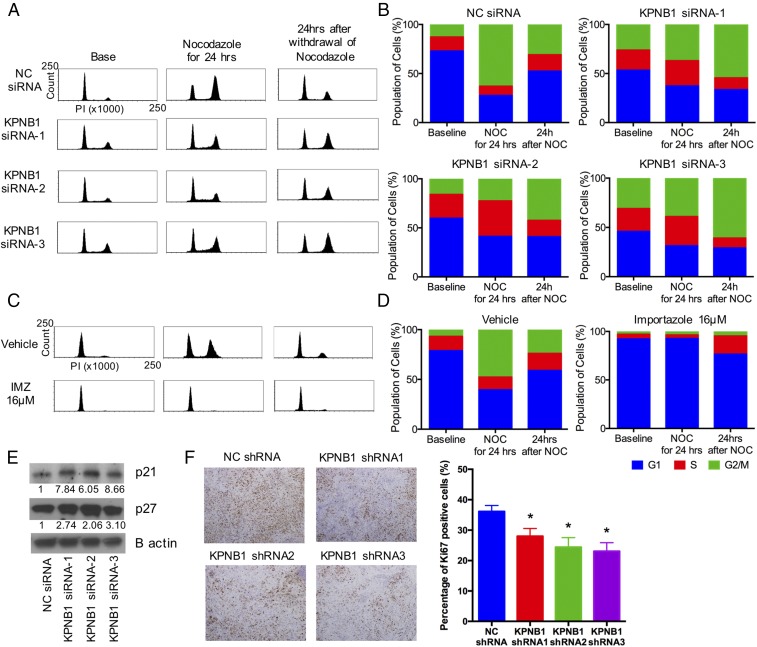
Fig. 4.
KPNB1 inhibition induces multiphase cell cycle arrest. (A and B) SKOV3 cells were transfected with NC siRNA or KPNB1 siRNA. (A) Two days later, cell cycles were assessed by flow cytometry (Left); then, to induce G2/M arrest, cells were treated with 500 ng/mL of nocodazole (NOC) for 24 h, and cell cycles were again assessed by flow cytometry (Middle); cells were then further incubated for 24 h after withdrawal of NOC and analyzed by flow cytometry (Right). (B) Cell populations at each stage of cell cycle are shown. (C and D) SKOV3 cells were treated with vehicle or 16 μM IMZ. (C) Two days later, cell cycles were assessed by flow cytometry (Left); then, to induce G2/M arrest, cells were treated with 500 ng/mL of NOC for 24 h, and cell cycles were again assessed by flow cytometry (Middle); cells were further incubated for 24 h after withdrawal of NOC and analyzed by flow cytometry (Right). (D) Cell populations at each stage of the cell cycle are shown. (E) SKOV3 cells were transfected with NC siRNA or KPNB1 siRNA. Three days after transfection, the expression levels of cell cycle-related proteins were assessed by Western blots. (F) SKOV3 cell were lentivirally transduced with NC shRNAs or KPNB1 shRNAs, and the transduced cells were i.p. injected into female nude mice. Six weeks after injection, i.p. tumors were collected and stained with Ki-67 (×40, scale bar, 100 μm) (Left). The proportions of Ki-67 positive cells are shown (n = 5 each, *P < 0.05 vs. NC shRNA) (Right).