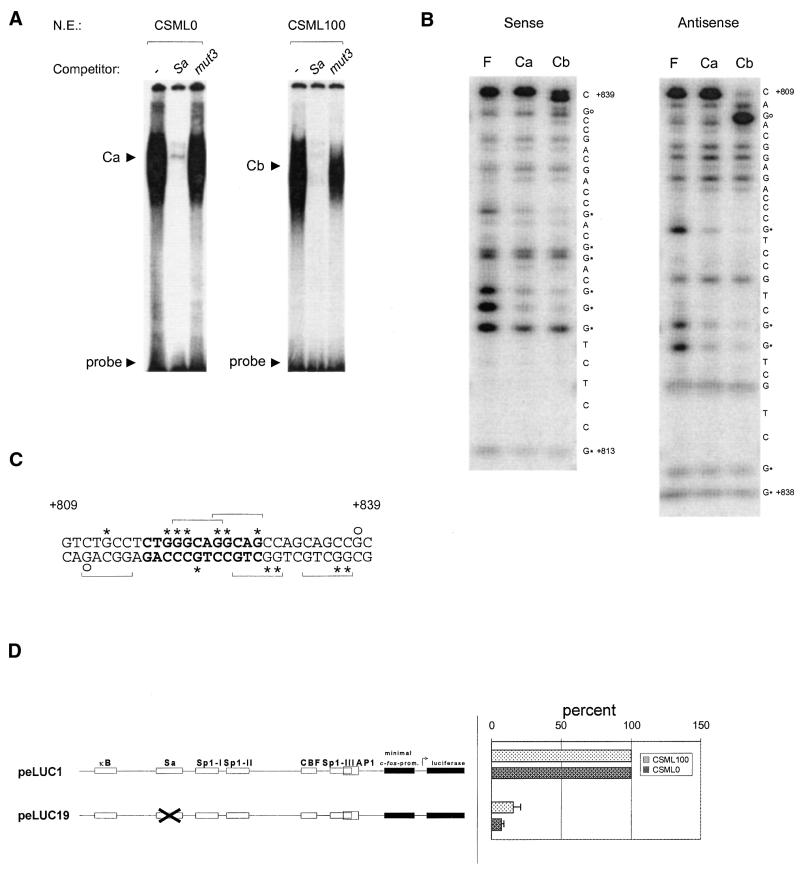
Figure 2.
The minisatellite-related sequence Sa contributes to S100A4 enhancer activity. (A) EMSA showing the complexes formed by Sa in CSML0 and CSML100 nuclear extracts. A Sa-containing 31mer, the Sa oligonucleotide, was end-labeled and analyzed by EMSA with CSML0 (5 µg) and CSML100 (10 µg) nuclear extracts. Competitor oligonucleotides Sa or mut3 were added as shown. (B) Methylation interference analysis of the Ca and Cb complexes. F, free DNA. Guanines involved in formation of the Ca and Cb complexes are marked by asterisks. Circles indicate the hyper-reactive nucleotides revealed by analysis of the Cb complex. (C) Summary of the methylation interference data. The Sa core sequence is shown in bold. The 5mer motifs, GGCA/TG, are indicated by horizontal brackets. Asterisks and circles are defined in the legend to (B). (D) The contribution of Sa to the activity of the S100A4 enhancer assayed in transient transfection of CSML0 and CSML100 cells with plasmid peLUC19. peLUC19 contains a mutated Sa site (mut3). The activity of peLUC19 in CSML0 and CSML100 cells is expressed as a percentage of the wild-type enhancer activity (peLUC1) in each cell line.