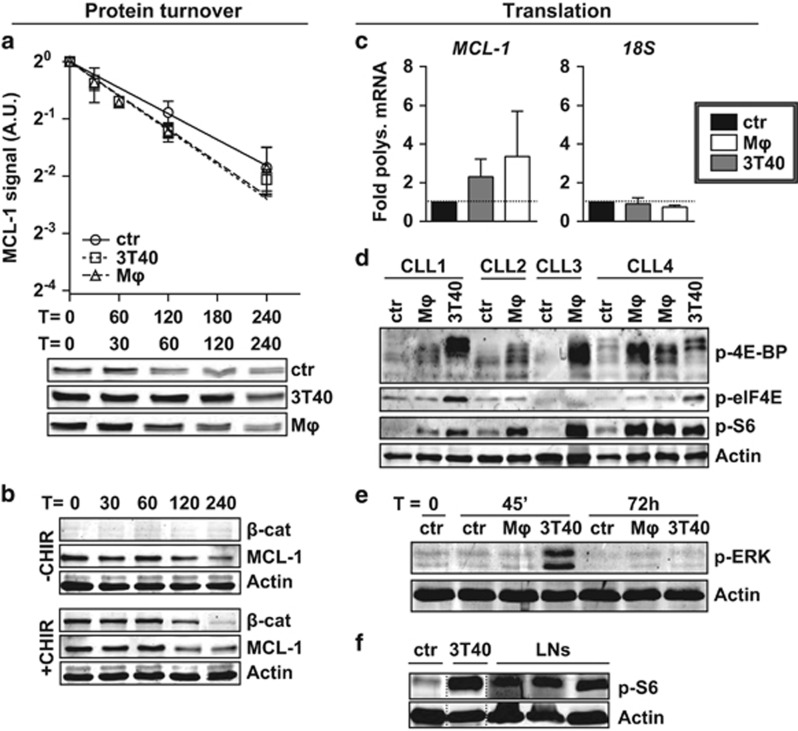
Figure 3.
MCL-1 is regulated on translational level. (a) After co-culture for 72 h, turnover of MCL-1 in CLL cells was determined by quantifying levels at different time points after addition of 25 μg/ml translation inhibitor cycloheximide, and compared with unstimulated samples (N=6). Each point represents mean±s.e.m. and regression lines were calculated using a best-fit exponential decay model fitted with the formula Y=Y0*ek*X, in which Y0 was set to 1. The best-fit k value was not significantly different between lines (upper panel). A representative turnover western blot for 1 CLL sample is shown (lower panel). Note the higher MCL-1 starting levels in the stimulated samples. A.U. denotes arbitrary units. (b) Unstimulated CLL samples were pre-treated or not treated for 1 h with 3 μM GSK3 inhibitor CHIR99021 before MCL-1 turnover was determined as in a. To exclude caspase-mediated MCL-1 breakdown, 5 μM Q-VD-OPh was added to all samples during culture when analyzed for MCL-1 levels by western blotting. A representative CLL sample of N=3 is shown. (c) The translational efficiency of MCL-1 mRNA was determined after 48 h co-culture by calculating the percentage of MCL-1 mRNA bound in polysomes, by performing qPCR on sucrose gradient-separated non-polysomal and polysomal fractions (see Materials and methods section and Supplementary Figure S4a). An MCL-1 and 18S qPCR were performed on pooled samples (polysomal/non-polysomal) and the relative amount of polysomal bound mRNA±s.e.m. (N=4 independent experiments) compared with the control condition (fold induction) was calculated for MCL-1 or 18S RNA. (d) CLL samples used in Figure 1b were again subjected to western blot and probed for phosphorylation of translation initiation factors and phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6, the latter is indicative of active translation. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Note that although the anti-p-4E-BP antibody was expected to detect only the slowest migrating form of 4E-BP, the non- and partially phosphorylated forms are also detected, most likely due to cross-reactivity to the unphosphorylated site. (e) The western blot presented in Figure 2c was probed for ERK phosphorylation (shown blot is representative of N=4). (f) Protein lysates from three CLL LN samples were analyzed by western blot for the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 as a measure for active translation. An unmatched unstimulated and 3T40-stimulated CLL sample were included for comparison.