Fig. 7.
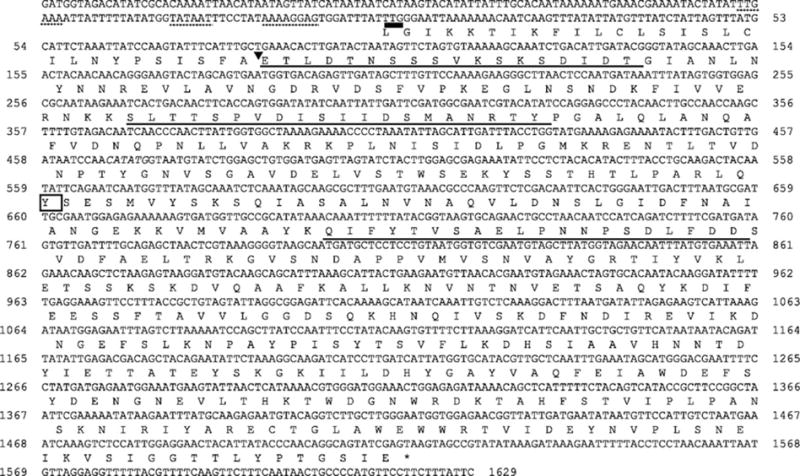
Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the 53-kDa sphaericolysin toxin and its amino acid sequence deduced from the nucleotide sequence. The underlined sequences were determined by Edman degradation. The putative Shine-Dalgarno, −10, and −35 sequences are indicated by the dotted lines. The bold line indicates the putative start codon of the precursor protein. An arrowhead indicates a possible cleavage point for the signal peptide that was predicted by employing the neural networks and hidden Markov models trained on sequences in the gram-positive-bacterium database. The NdeI site is indicated as italic characters (positions 467 to 472). A point mutation generated at position 159 is enclosed by a square. Nishiwaki et al. (2007). Copyright 2007 American Society for Microbiology.
