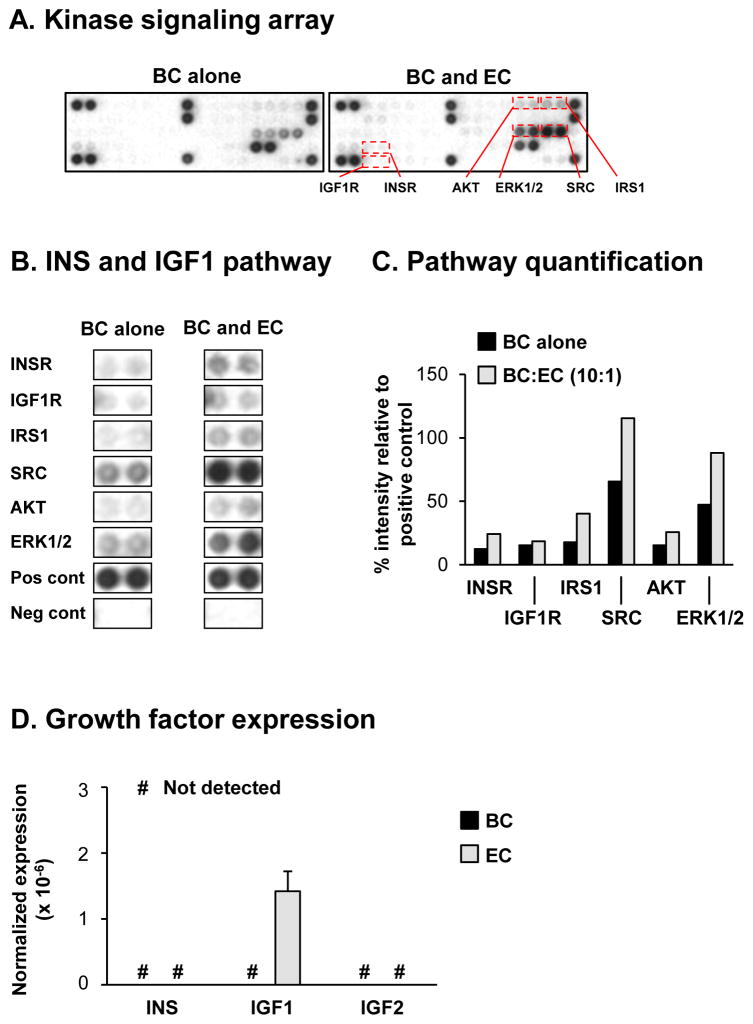
Figure 3.
Signaling via the insulin (INS) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) receptors (INSR and IGF1R) regulate basal cell (BC) differentiation into ciliated cells. A–C. Basal cells were cultured alone or co-cultured with EC at a 10:1 (BC:EC) ratio on air-liquid interface (ALI) culture for 7 days to assess the activity of specific kinase signaling pathways in BC in response to EC derived factors using the PathScan RTK Proteome Array (Cell signaling). A. Representative images from the same exposure times of the kinase signaling array from BC cultured alone and BC co-cultured with EC. B. Activity of the INS and IGF1 mediated signaling pathways including the receptor tyrosine kinases (ISNR and IGF1R) and downstream signaling nodes (IRS1, SRC, AKT and ERK1/2). “Pos cont” and “neg cont” represent the positive and negative control spots respectively on the array. C. Quantification of the INS and IGF1 signaling pathway activity. The intensities of spots were quantified with ImageJ and all values normalized by the positive control spots on the array (100%) and negative control spots (0%). D. TaqMan PCR analysis to assess mRNA expression of INS, IGF1 and IGF2 in BC (black bars) and EC (grey bars) following co-culture at ALI day 0. Bars indicate the mean expression for n=4 replicate wells and error bars indicate standard error of the mean.