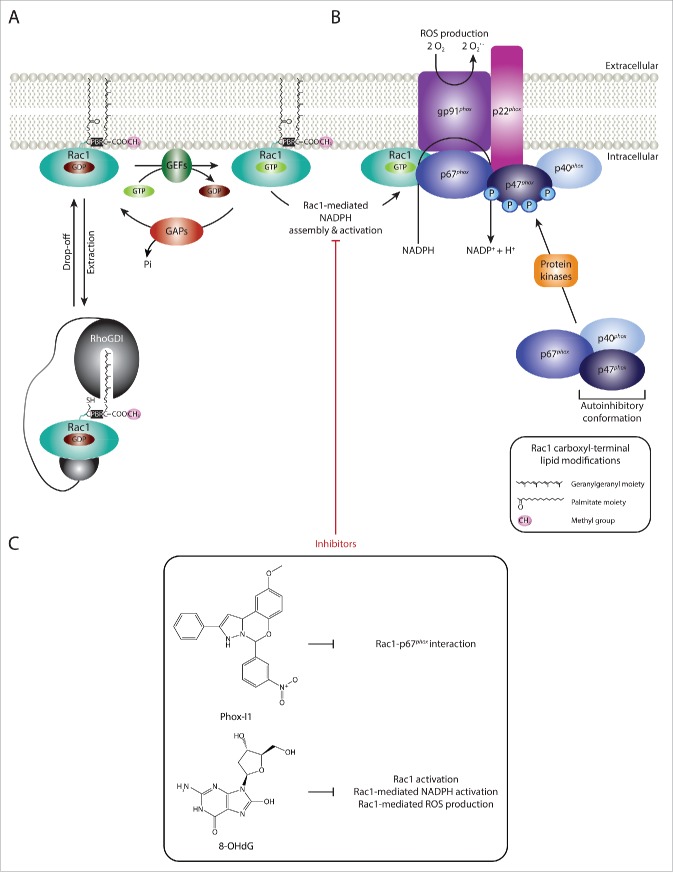
Figure 4.
Targeting Rac1-mediated assembly and activation of NADPH oxidases and ROS production. (A) Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) and Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (Rho GDIs) regulate Rac1 cycling from an inactive guanosine diphosphate (GDP)-bound state to an active guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-bound state. RhoGDIs also play a role in Rac1 cytoplasmic sequestration. (B) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases are multimeric protein complexes that transfer electrons from intracellular NADPH to extracellular molecular oxygen, generating superoxide anions (O2.−), a reactive oxygen species (ROS), in the process. Rac1 has been shown to regulate the assembly and activation of NADPH oxidases. For simplicity only one NADPH oxidase isoform, NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2), is depicted. Activation of the complex involves the assembly of the cytosolic regulatory proteins (p67phox, p40phox and p47phox) with the membrane-associated components (the catalytic subunit gp91phox and p22phox). This is mediated through the phosphorylation of the autoinhibitory region of p47phox, thereby releasing the autoinhibitory conformation and promoting p47phox-p22phox interaction. Additionally, activated Rac1 has been shown to directly bind to the p67phox subunit, thereby further facilitating complex assembly. Although not depicted in the figure, lipid metabolism within the plasma membrane also plays an important role in providing the anchoring sites for p40phox and p47phox. (C) Given the role of Rac1-mediated NADPH assembly and activation and ROS production in the progression of a number of human diseases, inhibitors that specifically target this Rac1 downstream signaling cascade have been identified. Phox-I1 represents a Phox-I class inhibitor that functions via blocking the interaction between Rac1 and p67phox, thereby inhibiting Rac1-mediated complex assembly. Another example includes 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), which also inhibits Rac1-medaited NADPH activation and ROS production. The chemical structures and mode of action of both compounds are outlined.