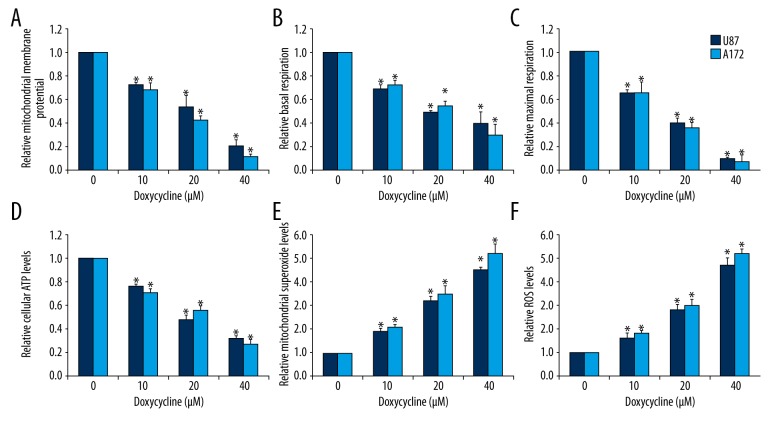
Figure 2.
Doxycycline significantly induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in glioblastoma cells. Doxycycline significantly decreases mitochondrial membrane potential (A), basal (B) and maximal OCR (C), and ATP levels (D) in A172 and U87 cells. Doxycycline significantly increases mitochondrial superoxide (E) and intracellular ROS (F) levels in A172 and U87. These data were derived from three independent experiments. The concentrations of pyrvinium and paclitaxel used in the combination studies were 0.1 μM and 0.5 μM, respectively. * p<0.05 compared to control.