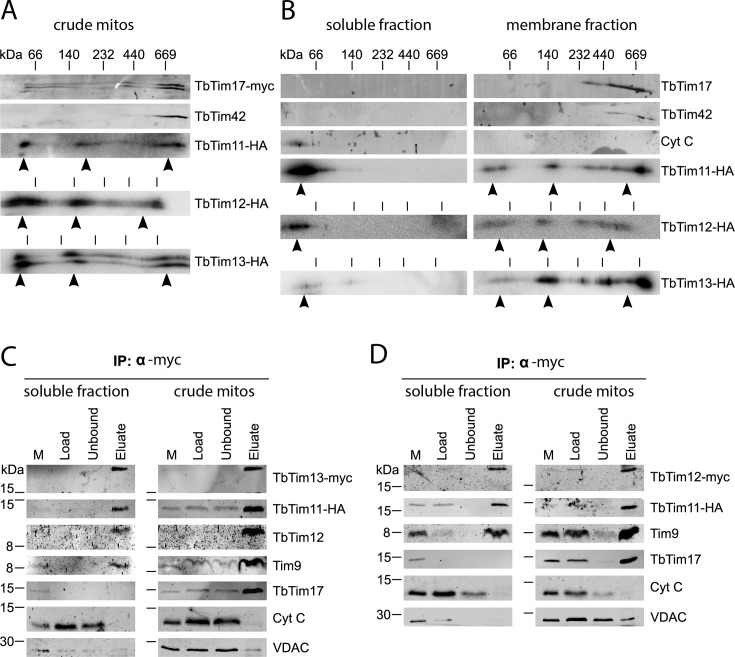
Fig 3. Small Tims form soluble complexes of approximately 70 kDa.
A) 2D BN-PAGE analysis of digitonin solubilized crude mitochondrial fractions. Lysates of cell lines expressing TbTim17-myc and one of the HA-tagged novel small Tims were combined and subjected to 6–16.5% BN PAGE in the first dimension, followed by 14% SDS PAGE in the second dimension and finally western blotting. The gels were aligned to the 66 kDa marker. The TIM complex components TbTim17-myc and TbTim42 were detected in all three analyses along with the respective HA-tagged small Tims. The control blots for the analyses of TbTim11-HA and TbTim13-HA can be found in S2 Fig. Arrowheads indicate the approximate positions of the high molecular weight complexes containing small Tim proteins. B) 2D BN-PAGE analysis of submitochondrial fractions. The soluble content of the IMS (“soluble fraction”) was separated from the “membrane fraction” using 0.1% digitonin. Solubilized proteins were separately subjected to 2D-BN/SDS-PAGE as described above. Cyt C serves as a marker for soluble IMS proteins. Arrowheads indicate high molecular weight complexes containing small Tim proteins. C) Co-immunoprecipitation from submitochondrial fractions targeting myc-tagged TbTim13. A cell line co-expressing TbTim11-HA and TbTim13-myc was used to prepare a crude mitochondrial fraction or a “soluble fraction” containing IMS proteins by differential digitonin extraction. 5% of the initial crude mitochondrial fraction (M) and the same amounts of “Load”, “Unbound” and “Eluate” as in Fig 2A were separated on SDS-PAGE and subjected to western blotting. The TIM complex component TbTim17 as well as the small Tims Tim9 and TbTim12 were detected by specific antibodies along with the HA- and myc-tagged other small Tims. The IMS protein Cyt C and the outer membrane protein VDAC were detected to confirm proper fractionation. D) Same experiment as in (C) targeting myc-tagged TbTim12 in a cell line co-expressing TbTim11-HA.