Fig. 6.
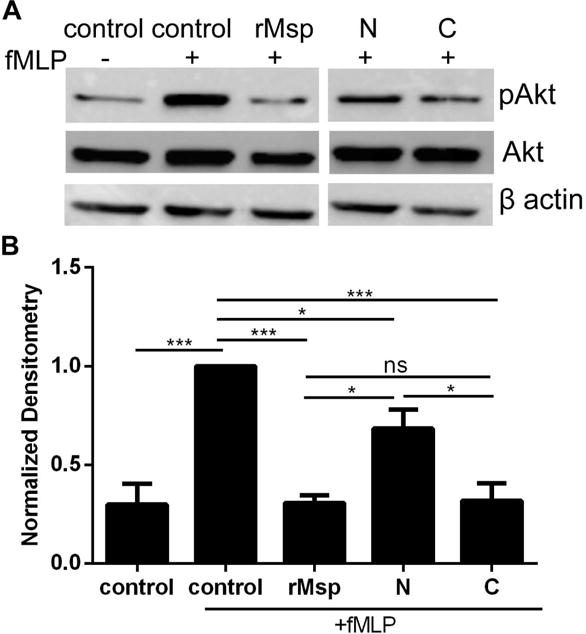
The C-terminal region of Msp impair Akt activation in response to fMLP. Neutrophils were treated with rMsp protein, N and C regions (30 μg/ml) for 30 minutes followed by stimulation with fMLP for 1 minute and lysis by boiling. Neutrophils alone or stimulated with fMLP were experimental controls. Phosphorylation of Akt was assessed as measure of Akt activation. A) The C region is more effective than the N region at inhibiting neutrophil phosphorylation of Akt. Representative western blots of cells lysates were probed with α-pAkt and α-total Akt, with α-β-actin as an additional loading control. B) Densitometry analysis of western blots was performed with ImageJ comparing pAkt to Akt. Results were normalized to Akt with the control + fMLP set to 1. Graphs represents mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 by unpaired t test).
