Fig. 7.
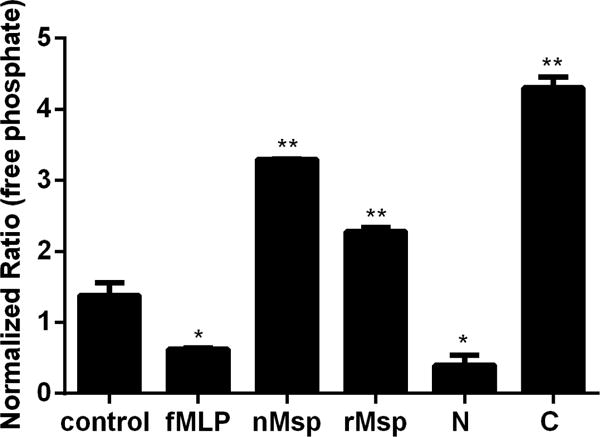
The C-terminal region of Msp increases PIP3 lipid phosphatase activity. Neutrophils were pretreated with nMsp, rMsp, N, and C or truncated Msp followed by assessment of phosphate release from a synthetic PIP3 substrate using a malachite green assay. Neutrophils alone and neutrophils stimulate with fMLP were experimental controls. Results were compared to the control alone, with the C region causing the most phosphate release. Graph represents the mean ± SEM of 1 of 3 independent experiments all showing the same results (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01 unpaired t test).
