Fig. 1.
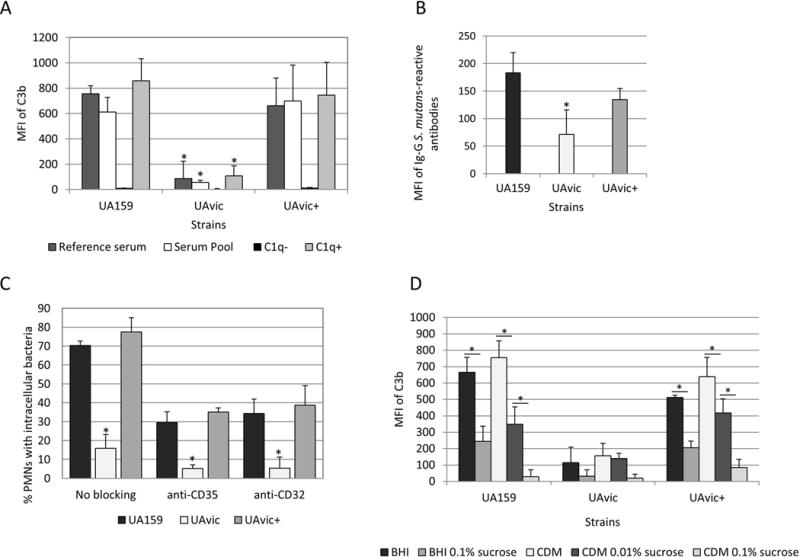
Comparisons of C3b deposition, IgG binding and opsonophagocytosis by PMN between the vicK mutant (UAvic) and parent (UA159) or complemented strain (UAvic+). Intensities of C3b deposition (A) or binding to serum IgG antibodies (B) were determined by flow cytometry (MFI) in strains treated with 20% human serum. A) Levels of surface C3b were measured after bacterial treatment with a reference serum, pools of sera obtained from six volunteers, commercial serum depleted of C1q (C1q−) and C1q− serum supplemented with purified C1q (C1q+). B) Binding to IgG was measured in strains treated with a reference serum. C) Percentages of PMN with internalized bacteria were determined after exposure of PMN isolated from peripheral blood to FITC-labeled bacteria in the presence of 20% serum. PMN treated with MAbs to block CR1 (CD35) or FcɤRIIa (CD32) receptors were used as control. D) Levels of C3b deposition were measured in strains grown in BHI or CMD supplemented or not with 0.01 to 0.1% sucrose. Columns represent means of three independent experiments. Bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate significant differences in relation to UA159 within the same condition (A-C) or between conditions under horizontal lines (D) (Kruskal-Wallis with post hoc Dunn’s test; p< 0.05).
