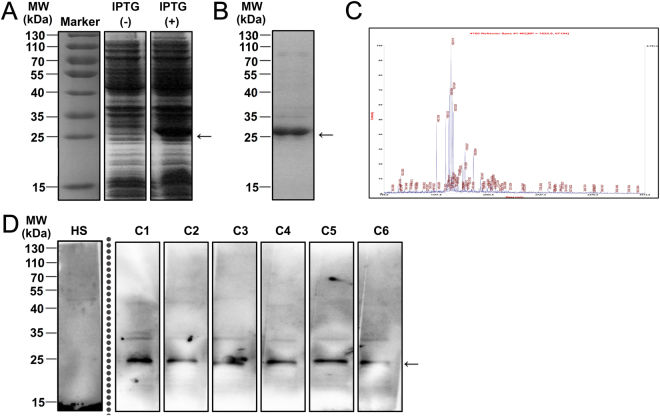
Figure 1.
Preparation of recombinant F. nucleatum-AhpC and identification of its immunogenic role in CRC patients. (A) Expression of recombinant Fn-AhpC after IPTG induction. The PCR amplified AhpC-DNA was inserted into pET28a vector before transformed into E. Coli BL21 strain. The expression of recombinant AhpC in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 0.5 mM IPTG was detected using 12% SDS-PAGE and Coomassie brilliant blue staining. (B) Purification of recombinant AhpC. The recombinant AhpC with a His tag was purified using a Ni-NTA column. (C) Identification of recombinant AhpC. The recombinant AhpC proteins were extracted from the gels stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R250, and subsequently digested with trypsin. The resulting peptides were further analysed using a MALDI-TOF/TOF analyser. (D) Antigens reactive with anti-AhpC-IgA were determined using western blotting. Recombinant AhpC were incubated with a reference dilution of pooled serum from 6 healthy subjects or separated serum from 6 Fn-positive CRC individuals as primary antibody. Notably, Fig. 1A,B and D were cropped from a single image on the dashed or solid lines to be better presented in the article’s context. The complete figures for Fig. 1A,B and D are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1A, Supplementary Fig. 1B and Supplementary Fig. 2, respectively.