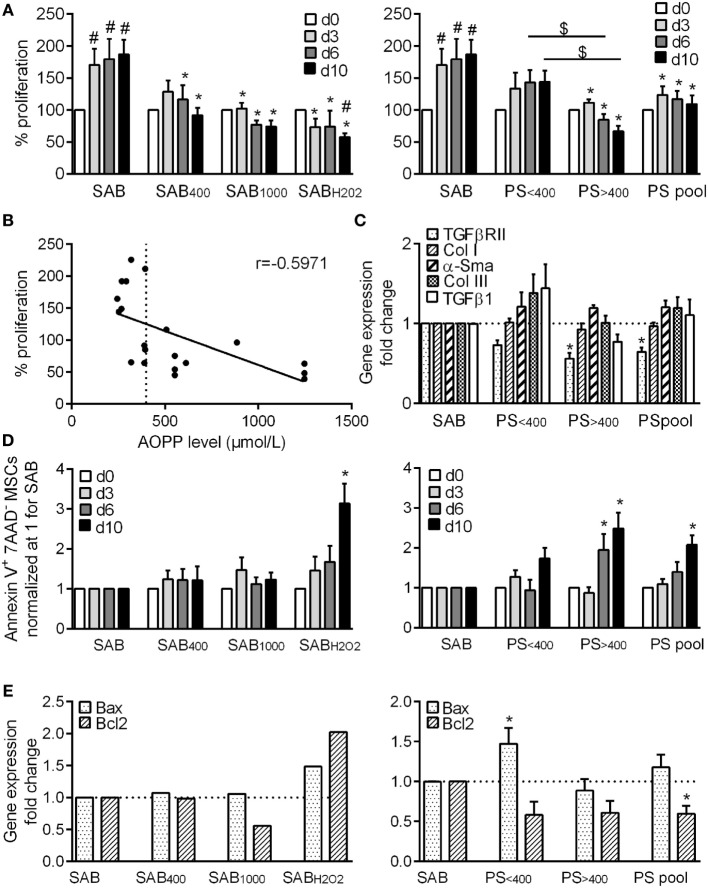
Figure 1.
HOCl- or H2O2-induced serum AOPPs and systemic sclerosis (SSc) patient serum decreased the proliferation rate of MSCs and increased the number of apoptotic MSCs. (A) Percentage of MSC proliferation depending on the concentration of advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) induced by HOCl in human serum AB (SAB): 400 µmol/L (SAB400) or 1,000 µmol/L (SAB10000), H2O2 (SABH2O2) (n = 8), or SSc patient serum at different time points: day 3, 6, and 10. Patient serum (PS) were divided in two groups depending on AOPP levels: <400 μmol/L (PS<400; n = 11) or >400 μmol/L (PS>400; n = 9) or pooled in a single group (PSpool; n = 20). Data were normalized to 100% of cells plated at day 0. (B) Linear regression curve between percentage of MSC proliferation and AOPP level in SSc patient serum at day 10 (n = 20). r indicated the Pearson’s correlation coefficient. (C) Gene expression fold change of different profibrotic markers (PS<400 and PS>400, n = 4; PSpool, n = 8). (D) Percentage of Annexin V+ 7-AAD- apoptotic MSCs at different time points (n = 8). (E) Gene expression fold change of proapoptotic marker Bax or antiapoptotic marker Bcl2 (PS<400 and PS>400, n = 4; PSpool, n = 8). Data were normalized to 1 for MSCs in SAB-containing medium. #p < 0.05 versus day 0; *p < 0.05 versus SAB at same time point; $p < 0.05 versus indicated condition.