Fig. 1.
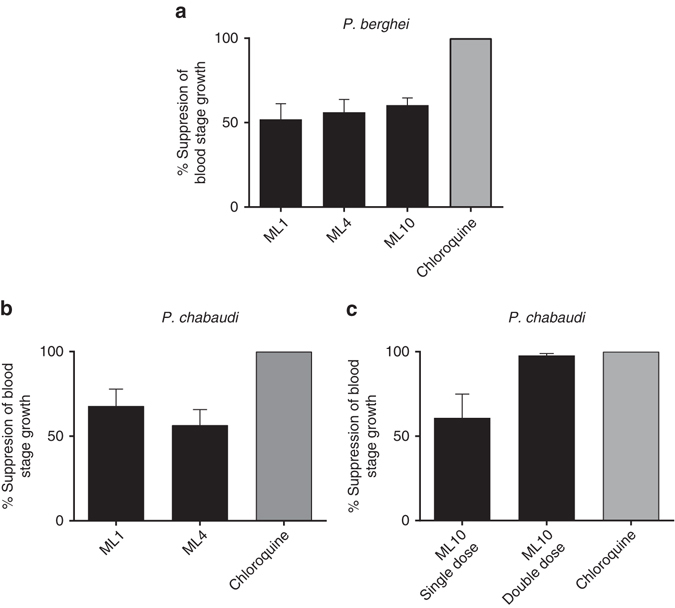
In vivo efficacy of PKG inhibitors against rodent malaria parasites. a Groups of five female BALB/c mice were infected with 1x107/ml P. berghei (ANKA) blood stage parasites in a Peters 4-day test and were given a twice daily dose (25 mg/kg) of one of three test compounds by oral gavage. Chloroquine was used as a positive control at a single daily oral dose of 10 mg/kg. b Groups of five female BALB/c mice were infected with 1×107 P. chabaudi (AS) blood stage parasites and were given a single oral dose (50 mg/kg) of either ML1 or ML4 by oral gavage just prior to the predicted onset of schizogony. Chloroquine was used as a positive control at a single daily oral dose of 10 mg/kg. c Groups of five BALB/c mice were infected with 1×107 P. chabaudi (AS) blood stage parasites and were given either a single or twice daily oral dose (50 mg/kg) of ML10 by oral gavage. The first dose was given to both groups of mice just prior to the predicted onset of schizogony and in one group this was followed 3 h later when schizogony was predicted to have been completed. The data are from single experiments each performed on a group of five mice. Error bars show the s.e.m
