Fig. 3.
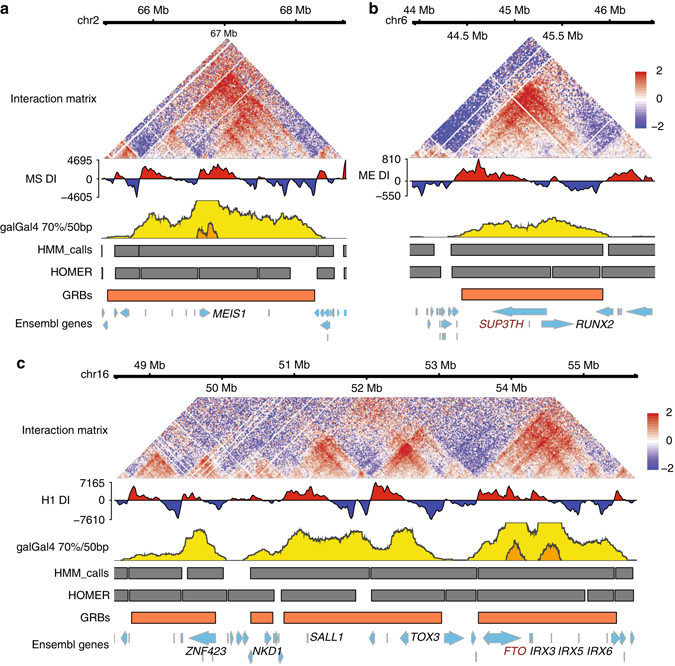
Examples of genomic regulatory blocks and their associated interaction landscapes in human. GRBs at several human loci show strong association with the structure of regulatory domains proposed from Hi-C. a The GRB containing MEIS1 (chr2:65270920-68723490) accurately predicts the span of regulatory interactions defined by Hi-C. b The region located at chr6-44198640-46071520 contains both the transcription factor RUNX2 and its bystander gene SUP3TH (shown in brown), both of which are located within a GRB which predicts the topological organisation of the locus. c A region located on chr16:48476700-55776880 in hg19 contains several GRBs containing important developmental regulators, including IRX3/5/6, TOX3, SALL1, NKD1 and ZNF423, which exhibit strong concordance with TADs. The IRX3/5/6 locus contains homeobox proteins which have multiple functions during animal development and contains a well-known bystander gene FTO (shown in brown), which contains an intronic enhancer which drives expression of IRX3 38–41
