Figure 6.
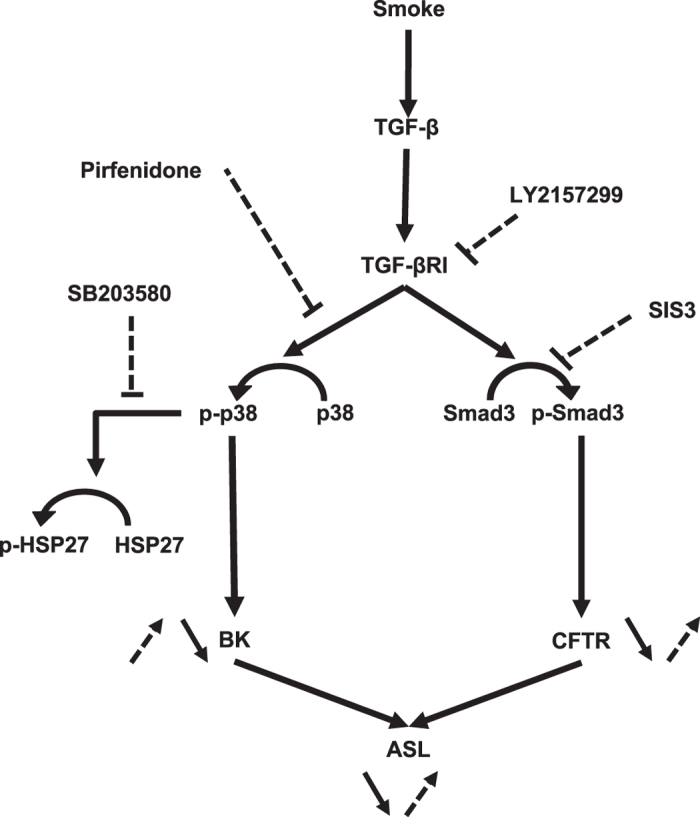
Schematic diagram of smoke effects on CFTR and BK activities as well as ASL volume in the absence or presence of different inhibitors. Smoke (black arrow), stimulates both Smad3 and p38 phosphorylation via TGF-β signalling, which in turn decreases CFTR and BK channel functions. Overall this causes ASL volume loss, resulting in mucociliary dysfunction. Inhibitors (dotted arrow) used for the presented experiments ameliorated CFTR and BK activities and thereby improved ASL volume loss.
