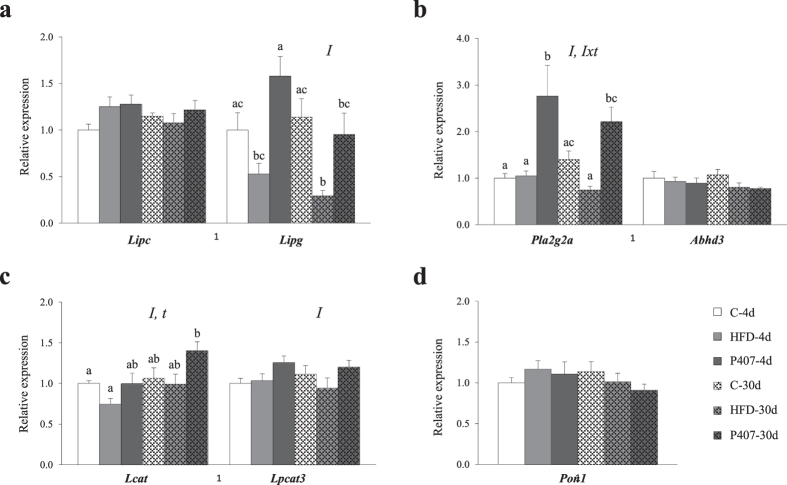
Figure 3.
Relative expression levels of hepatic genes implicated in the regulation of the circulating Lyso-PL levels. (a) Lipases: Lipc, hepatic lipase; Lipg, endothelial lipase. (b) Phospholipases: Pla2g2a, phospholipase A2 group IIA; Abhd3, abhydrolase domain-containing 3. (c) Acyltransferases: Lcat, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; Lpcat3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3. (d) Pon1, Paraoxonase 1. The hamsters were assigned to six groups, depending on the pro-dyslipidemic treatment and duration of the experiment: control group-4 days (C-4d), high-fat diet-4 days (HFD-4d), pro-dyslipidemic agent-4 days (P407-4d), control group-30 days (C-30d), high-fat diet-30 days (HFD-30d), and pro-dyslipidemic agent-30 days (P407-30d). Total RNA was isolated from the liver and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. The relative expression levels were determined using β-actin as the reference gene and were normalized to the C-4d group. The data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 9–10). The statistical comparisons among groups were conducted using two- and one-way ANOVAs. I: the effect of the intervention (HFD and P407); t: the effect of time; Ixt: the interaction between the two factors (two-way ANOVA, p < 0.05). For each gene, different superscript lowercase letters (a,b,c) indicate significant different mean values (one-way ANOVA and Games-Howell post hoc test, p < 0.05).