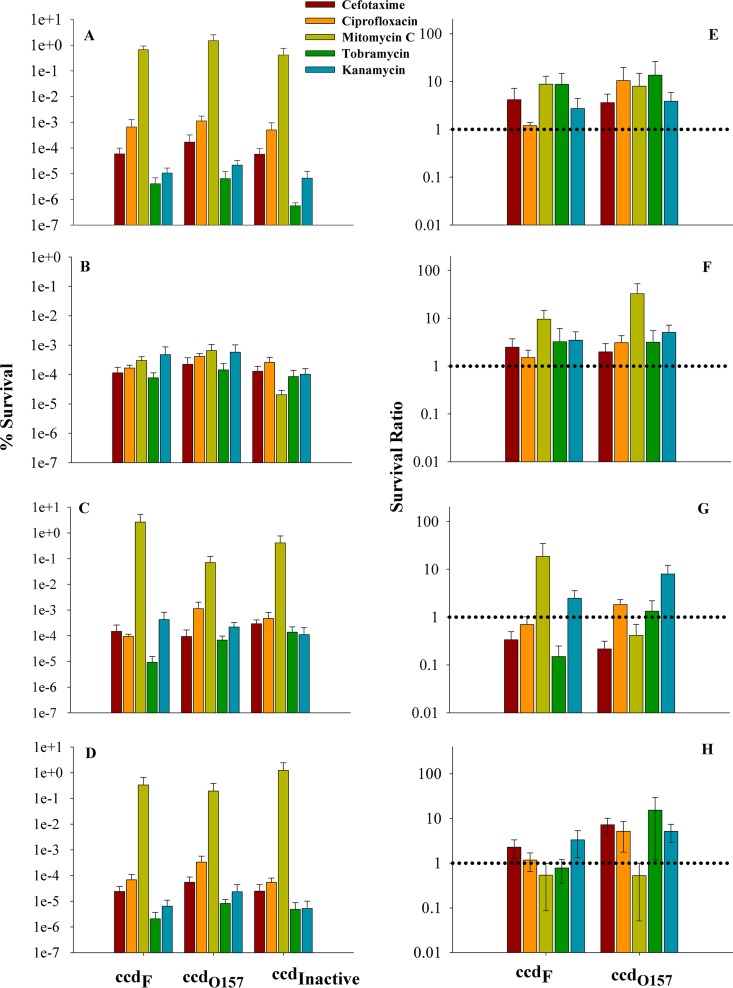
FIG 1.
Survival of E. coli strains containing the ccd operon upon antibiotic exposure. The BW25113 strains BW25113 ccdO157, BW25113 ccdF, and BW25113 ccdInactive were first exposed to a prestress that involved either heat or a sublethal dose of ampicillin or ciprofloxacin. Survival of these strains was monitored in the presence of various antibiotics. Percent survival was calculated for each strain as the ratio of CFU after antibiotic exposure to CFU prior to antibiotic exposure. The survival ratio was calculated as the ratio of the percent survival of a strain containing active ccd to the percent survival of the reference strain containing inactive truncated ccd (BW25113 ccdInactive). (A to D) Percent survival of E. coli strains BW25113 ccdO157, BW25113 ccdF, and BW25113 ccdInactive in the presence of heat or a sublethal dose of ampicillin or ciprofloxacin or without prestress, respectively. (E to H) Survival ratios of E. coli strains BW25113 ccdO157 and BW25113 ccdF in the presence of heat or a sublethal dose of ampicillin or ciprofloxacin or without prestress, respectively. The y axis is shown on a log scale, and error bars indicate the standard error from 4 independent experiments. Each experiment was done using three biological replicates. The survival ratio for strain BW25113 ccdO157 in the absence of prestress is higher than that for strain BW25113 ccdF against cefotaxime, ciprofloxacin, tobramycin, respectively. Survival of both strains BW25113 ccdO157 and BW25113 ccdF is greater than that of strain BW25113 ccdInactive for most antibiotics, as indicated by the dotted lines.