FIGURE 1.
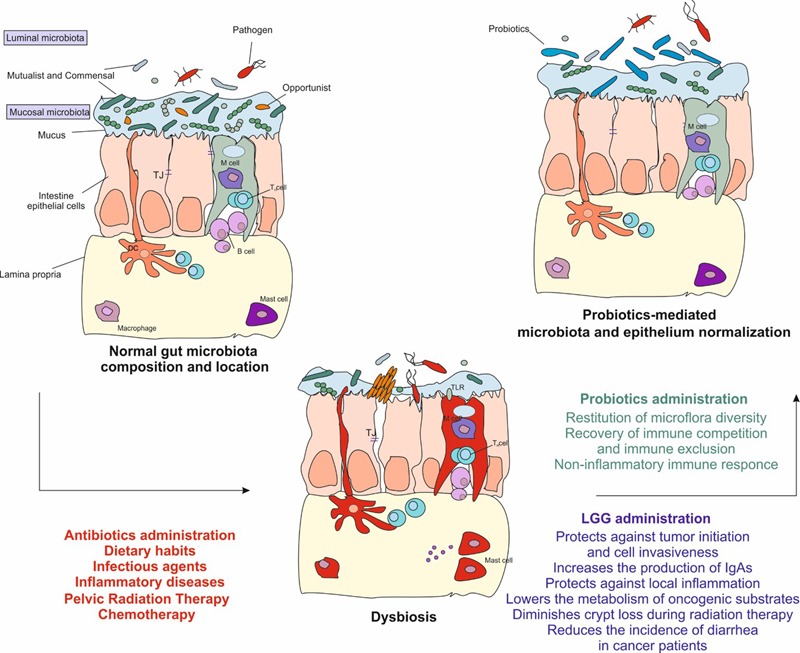
The gut microbiota is fundamental to maintain the intestinal homeostasis. Infectious agents, unhealthy dietary habits, antibiotics, radiation, and chemo or immunotherapy cause the depletion of resident microorganisms. This alteration gives the chance to the transient microbiota, which includes pathogen and opportunistic microorganisms, to breach through the epithelium resulting in a dysbiosis state displayed by abdominal pain, discomfort, bloating, and diarrhea. Dysbiosis eventually leads to the activation of the inflammatory response, to epigenetic modifications and to tissue damage. Administration of probiotics helps to restore the depletion of the gut microbiota and reduces the inflammation. In particular, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG may be helpful in those patients undergoing anti-cancer treatments. It protects against tumor onset and invasiveness, lowers the metabolism of oncogenic substrates, increases the production of IgAs, protects against local inflammation, diminishes crypt loss and apoptosis during radiation therapy. Finally, it has shown to be helpful in reducing diarrhea severity and incidence in cancer patients. TJ, tight junction; DC, dendritic cell; LGG, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.
