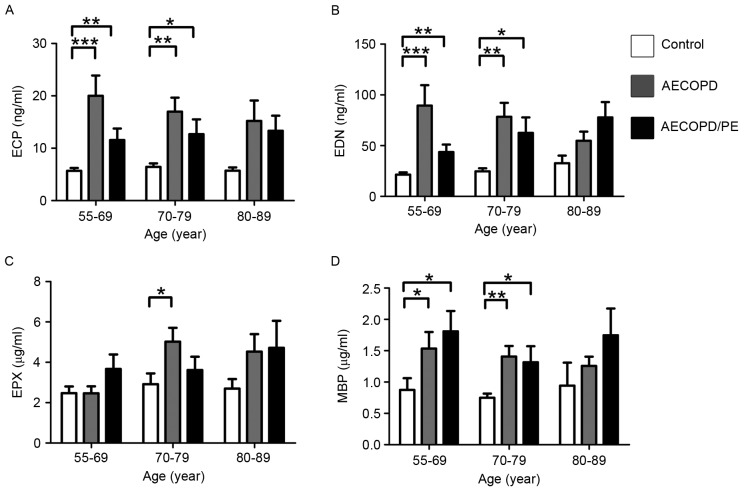
Figure 4.
Levels of (A) ECP (*P<0.05 vs. AECOPD/PE at ECP in the 70–79 age group; **P<0.01 vs. AECOPD/PE at ECP in the 55–69 age group and AECOPD at ECP in the 70–79 age group; ***P<0.001 vs. AECOPD at ECP in the 55–69 age group), (B) EDN (*P<0.05 vs. AECOPD/PE at EDN in the 70–79 age group; **P<0.01 vs. AECOPD/PE at EDN in the 55–69 age group and AECOPD at EDN in the 70–79 age group; ***P<0.001 vs. AECOPD at EDN in the 55–69 age group), (C) EPX (*P<0.05 vs. AECOPD at EPX in the 70–79 age group), and (D) MBP classified by age in normal controls and patients with AECOPD/PE or with AECOPD (*P<0.05 vs. AECOPD/PE at MBP in the 55–69 and 70–79 age groups, and vs. AECOPD at MBP in the 55–69 age group; **P<0.01vs. AECOPD at MBP in the 70–79 age group). Normal controls (ages 55–69, n=16; ages 70–79, n=16; ages 80–89, n=3); patients with AECOPD (ages 55–69, n=10; ages 70–79, n=21; ages 80–89, n=16); patients with AECOPD/PE (ages 55–69, n=12; ages 70–79, n=13; ages 80–89, n=5). ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; EPX, eosinophil peroxidase; MBP, major basic protein; AECOPD, acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; PE, pulmonary embolism.