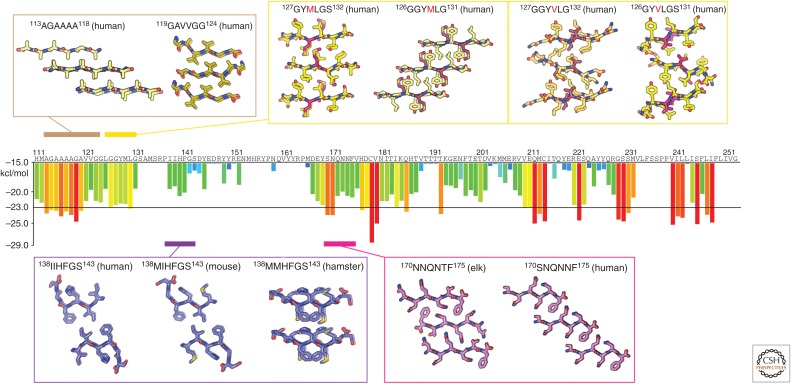
Figure 3.
Atomic structures of PrP steric zippers. The propensity for any given six-residue segment in the sequence of human PrP to form a steric zipper was estimated using the ZipperDB database (http://services.mbi.ucla.edu/zipperdb/). The evaluation of a single six-residue segment gives an energy score shown in kcal/mol on the bar graph axis (left). A colored bar representing each score is assigned to the first residue of each six-residue window throughout the PrP sequence. More negative scores are more favorable, and segments with a score of less than −23 kcal/mol are the most likely to form zippers. Atomic structures of zipper-forming segments from four regions of the sequence are shown. Two structures of the human sequence cover the region residues 113–124. Several structures cover residues 126–132 and contain either a methionine or valine at position 129. Structures from human, mouse, and hamster sequences span residues 138–143. Two structures—one with an elk sequence and the other human—span residues 170–175. As indicated in Table 1, numbers correspond to the human sequence.