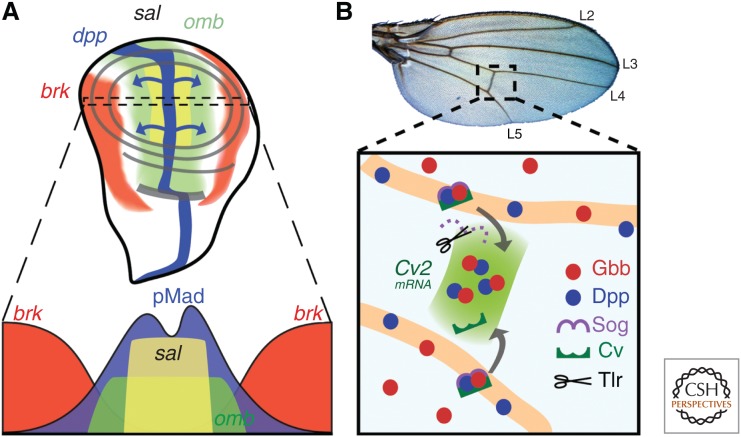
Figure 3.
Dpp signaling during Drosophila wing development. (A) During larval development, dpp (blue, top) is expressed along the A/P border and its gene product spreads to both compartments (blue arrows). High Dpp signaling in the middle of the disc results in activation of Mad (blue, below), which silences brk (red). The inverse gradients of pMad and Brk form the nested expression pattern of sal and omb. pMad is slightly lower in cells abutting the A/P axis due to local tkv down-regulation (Funakoshi et al. 2001). (B) Posterior crossvein (PCV) forms between the L4 and L5 veins (top), which begins during pupal development. Dpp–Gbb heterodimers bound by Sog (purple) and crossvein (dark green) allow for facilitated diffusion of ligands into the presumptive PCV space. Tolloid-related (Tlr) cleaves Sog and allows for signaling to occur. The initial broad signaling induces expression of CV-2, which further sharpens the signaling, resulting in PCV formation.